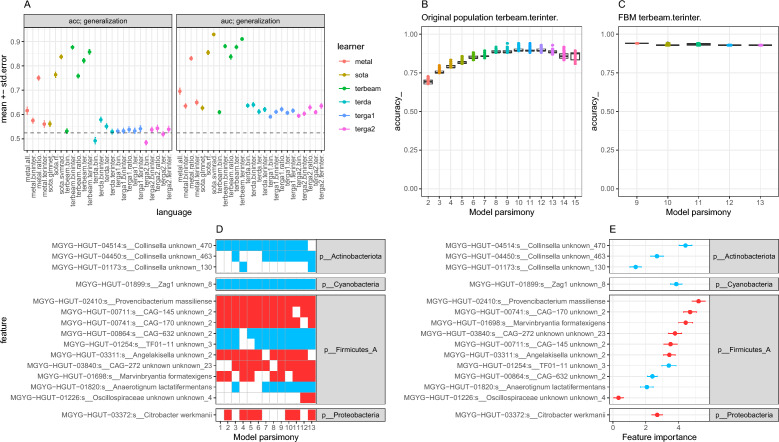
Figure 5.
Prediction of T2DM state from taxonomic prevalence based on Predomics models. (A) mean ± standard error of accuracy (acc) and AUC of T2DM predictions of best models based on 26 different learners integrated into the Predomics package from 10 times tenfold cross-validation schema from species presence/absence data. The dashed line represents the majority class (i.e., the accuracy obtained when simply predicting the T2DM status through chance alone; 0.52). Predictions from terbeam learner and terinter language show the best performance in comparison with other BTR models considering AUC and accuracy (acc). (B) Boxplots of the accuracy (y-axis) of terbeam-terinter models (n = 1316) at different model sparsities (number of features per model; x-axis). (C) Same as the B panel for the Family of Best Models (FBM; n = 13 terbeam-terinter models whose accuracy is within a given window of the best model’s accuracy). (D) Heatmap representing the prevalence of the 14 bacterial species (y-axis) included in the 13 models in the FBM (red = presence and more prevalent in T2DM group; blue = presence and more prevalent in control group; white = absence). (E) Mean ± standard error of feature importance variable (decrease accuracy when the feature is removed in cross-validation process) for the 14 bacterial species included in the terbeam-terinter FBM (red = high mean prevalence in the T2DM group; blue = High mean prevalence in the control group).