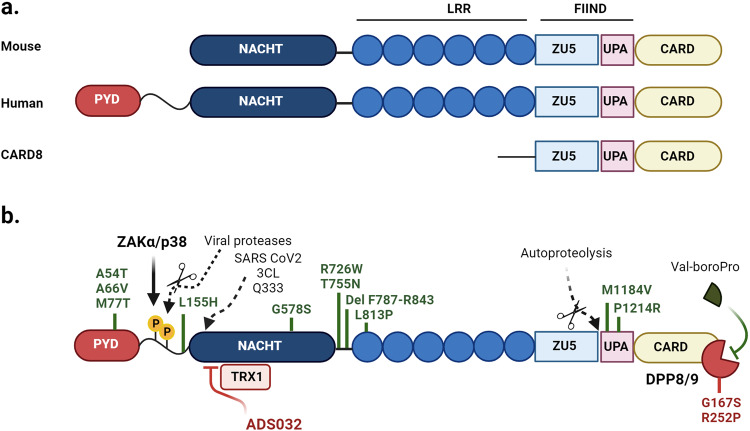
Fig. 1. Schematic representation of NLRP1.
a A comparison of architectural differences between mouse and human NLRP1. b Representation of the activating and restraining/inhibitory functions of NLRP1. Consistent between species, NLRP1 is constrained in an inactive form via DPP8/9 interaction with the FIIND domain, the inhibition of which by Val-boroPro (also called Talabostat) disengages DPP8/9 association inducing functional degradation and subsequent formation of an active inflammasome complex, while oxidized thioredoxin restrains NLRP1 activity via interaction with the NACHT-LRR domain. NLRP1 is also restrained by thioredoxin-1 (TRX1) which interacts with the NACHT/LRR domains while in response to ribotoxic stress, ZAKα and p38 MAP kinase induce phosphorylation of the disordered inter-region between the Pyrin and NACHT domains, mediating activation of NLRP1 and formation of a functional inflammasome complex. The small compound inhibitor ADS032 targets the Walker B motif within the NACHT domain to inhibit NLRP1 activation. The role of NLRP1 in disease is highlighted by gain of function mutations (marked in green: refer to Supplementary Table 1) in functional domains of NLRP1, while a loss of function variant in DPP8/9 (red) induces constitutive NLRP1 activity.