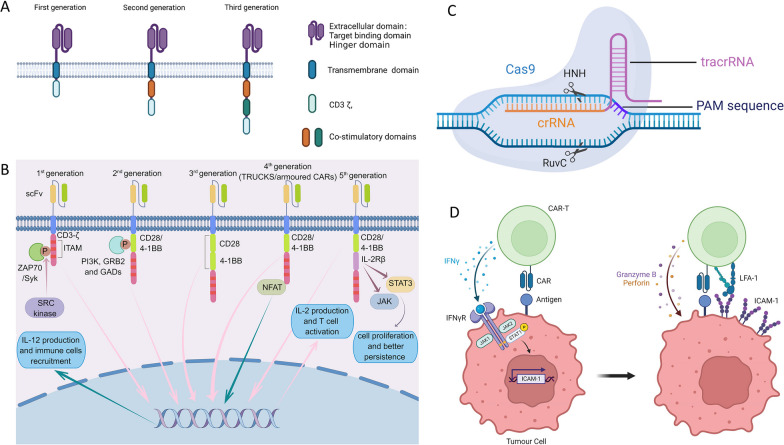
Fig. 3.
CAR structure and stimulation mechanism. A The basic structure of CARs mainly consists of four sections: (i) the target binding domain, linked to the intracellular section by the hinger domain, is located extracellularly to recognize the specific antigen on the tumor surface; (ii) the transmembrane domain; (iii) the CD3ζ signaling domain; and (iv) the costimulatory domain, mainly the molecule 4-1BB or CD28, which encourages intracellular transduction of stimulatory signals. Reproduced under the terms Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0) (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)[178]. Copyright 2022, The Authors, published by BioMed Central. B CAR activates the second messenger molecules in the tyrosine kinase signaling pathway by cascading phosphorylation after identifying TAAs on the surface of tumors, thus stimulating intranuclear genes to express the inflammatory factor IL-2 and promote T cell activation. Furthermore, the fourth generation utilizes NFAT to stimulate inflammatory factor IL-12 production and recruit more immune cells, and the fifth generation utilizes the JAK-STAT pathway to prove T cell proliferation and achieve better persistence. Reproduced under the terms CC BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/) [179]. Copyright 2022, The Authors, published by BioMed Central. C CRISPR/Cas9 is a popular tool for editing CAR-T cell genes: crRNA supports target sequence identification; tracrRNA supports structural stability of the complex; protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) sequence assists in locating the target sequence; HNH and RuvC nuclease domains cut target and nontarget DNA strands, respectively. Reproduced under the terms CC BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/) [181]. Copyright 2022, The Authors, published by BioMed Centra. D CAR-T cells release the inflammatory factor IFNγ, stimulating the tumor cell IFNγR signaling pathway, which mediates intercellular adhesion, is critical in the interaction between CAR-T cells and solid tumors and ultimately ensures the cytotoxicity of granzyme B and perforin. Reproduced under the terms CC BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/) [210]. Copyright 2022, The Authors, published by Frontiers