Fig. 1. De novo assembly outcome.
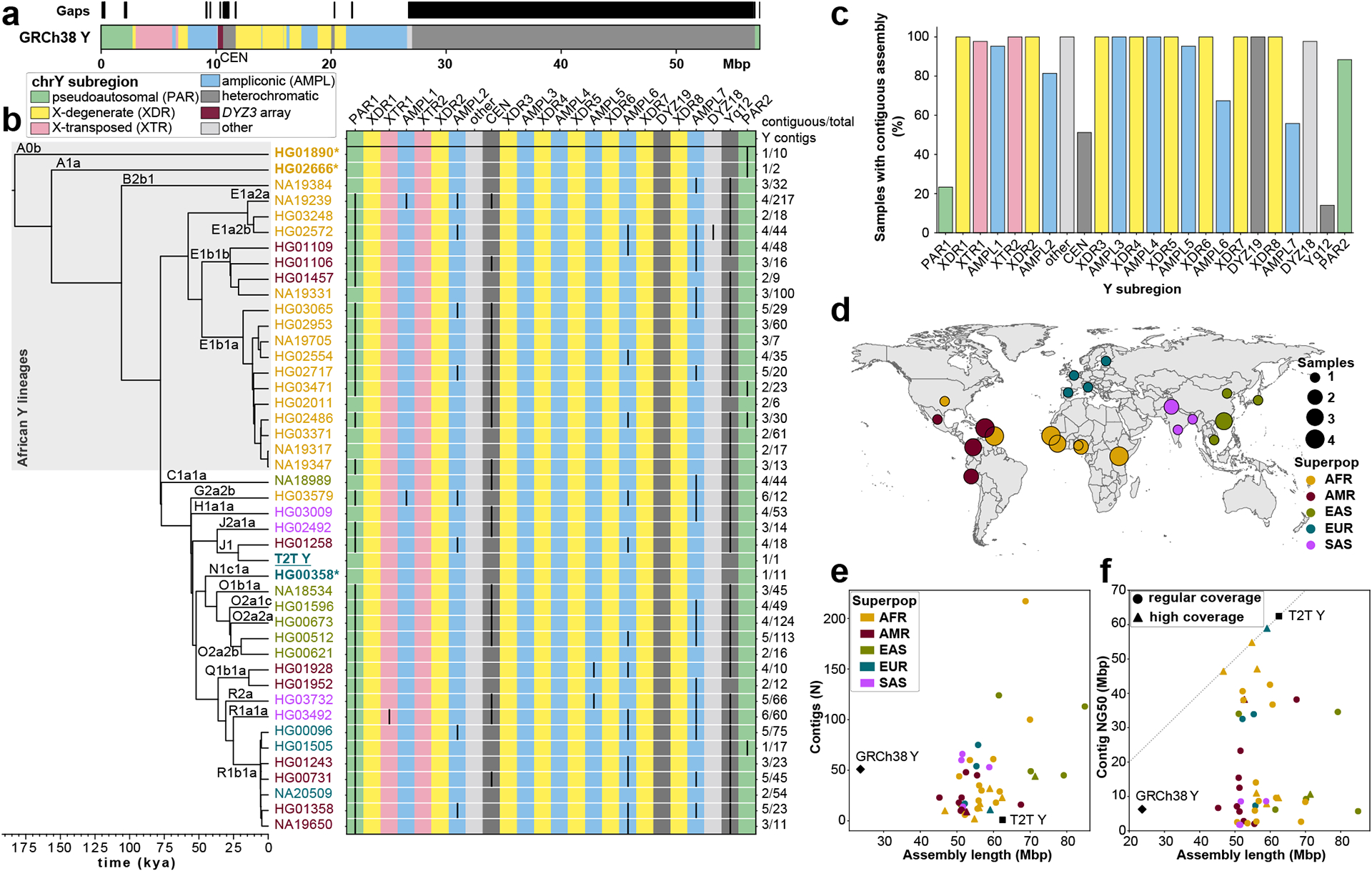
a. Human Y chromosome structure based on the GRCh38 Y reference sequence.
b. Phylogenetic relationships (left) with haplogroup labels of the analysed Y chromosomes with branch lengths drawn proportional to the estimated times between successive splits (see Fig. S1 and Table S1 for additional details). Summary of Y chromosome assembly completeness (right) with black lines representing non-contiguous assembly of that region (Methods). Numbers on the right indicate the number of Y contigs needed to achieve the indicated contiguity/total number of assembled Y contigs for each sample. CEN - centromere - includes the DYZ3 α-satellite array and the pericentromeric region. Three contiguously assembled Y chromosomes are in bold and marked with an asterisk (assemblies for HG02666 and HG00358 are contiguous from telomere to telomere, while HG01890 assembly has a break approximately 100 kbp before the end of PAR2) and the T2T Y is in bold and underlined. The colour of sample ID corresponds to the superpopulation designation (see panel d). Note - GRCh38 Y sequence mostly represents Y haplogroup R1b.
c. The proportion of contiguously assembled Y-chromosomal subregions across 43 samples.
d. Geographic origin and sample size of the included 1000 Genomes Project samples coloured according to the continental groups (AFR, African; AMR, American; EUR, European; SAS, South Asian; EAS, East Asian). Superpop - super population.
e. Y-chromosomal assembly length vs. number of Y contigs. Gap sequences (N’s) were excluded from GRCh38 Y.
f. Y-chromosomal assembly length vs. Y contig NG50. High coverage defined as >50⨉ genome-wide PacBio HiFi read depth. Gap sequences (N’s) were excluded from GRCh38 Y.
