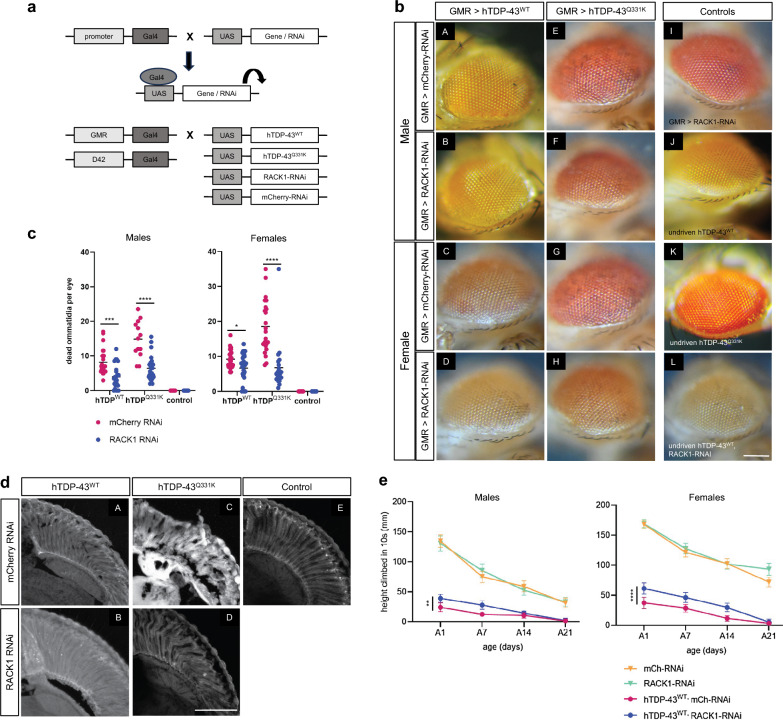
Fig. 9.
RACK1 knockdown significantly reduces hTDP-43-induced neuronal death and dysfunction in transgenic D. melanogaster. a Schematic illustration for the construction of transgenic D. melanogaster lines specifically targeting retinal (GMR-driven) or motor (D42-driven) neurons. b Representative images of fly eyes. Expression of hTDP-43WT (A–D) or hTDP-43Q331K (E–H) in retinal neurons cause neuronal death in both males and females, detected as darkened ommatidia. RACK1-RNAi reduces the appearance of dead ommatidia in all four conditions (B, D, F, H), compared to mCherry-RNAi control (A, C, E, G). Control flies with no dead ommatidia include those expressing RACK1-RNAi alone (I), and those harbouring unexpressed (undriven) transgenes (J–L). Scale bar: 250 mm. c Quantification of retinal neuronal death. Mann–Whitney test indicates a significant reduction in ommatidia death upon RACK1-RNAi KD in both males and females expressing either hTDP-43WT or hTDP-43Q331K. 21–33 flies were scored per condition. Statistics: Mann–Whitney test, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001. ****p < 0.0001. d Histological analysis of retina from flies expressing hTDP-43WT (A, B) or hTDP-43Q331K (C, D) in conjunction with control mCherry-RNAi (A, C) or RACK1-RNAi (B, D) show preservation of retinal architecture by RACK1 KD. Scale bar: 50 mm. e Both male and female hTDP-43WT transgenic flies show reduced climbing ability compared to mCherry-RNAi controls, which was significantly improved by RACK1-RNAi. Statistics: 2-way ANOVA. **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001. 60–100 flies were scored per condition. Error bars: SD