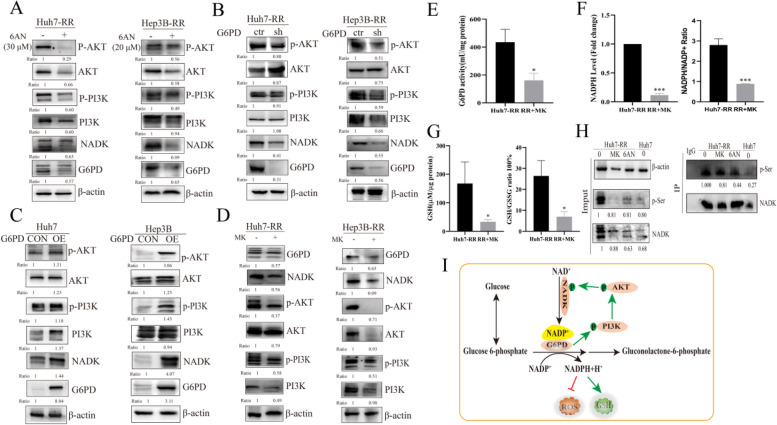
Fig. 5.
A feedback loop of PPP and PI3K/AKT signal pathway drives regorafenib-resistance in HCC. A The effects of G6PD inhibition by 6AN on the expression of NADK and activation of PI3K/AKT signal pathway in drug-resistant cells, n = 4. B The effects of G6PD knockdown on the expression of NADK and activation of PI3K/AKT signal pathway in drug-resistant cells, n = 3. C The effects of G6PD overexpression on the expression of NADK and activation of PI3K/AKT signal pathway in drug-sensitive cells, n = 3. D. The effects of PI3K/AKT signal pathway inhibition by MK-2206(MK, 10 μM) on the expression of G6PD and NADK in drug-sensitive cells, n = 3, n = 3. E The effects of PI3K/AKT signal pathway inhibition by MK (10 μM) on G6PD enzymatic activity in regorafenib-resistant cells, n = 3 (Huh7 cell line). F The effects of PI3K/AKT signal pathway inhibition by MK (10 μM) on NADPH level (left) and NADPH/NADP+ ratio (right) in drug-resistant cells, n = 3 (Huh7 cell line). G The effects of PI3K/AKT signal pathway inhibition by MK(10 μM) on GSH level (left) and GSH/GSSG ratio (right) in drug-resistant cells, n = 3 (Huh7 cell line). H The effects of PI3K/AKT signal pathway by MK (10 μM) or G6PD inhibition by 6AN (30 μM) on phosphorylation level of NADK were detected by immunoprecipitation in drug-sensitive and regorafenib-resistant cells, n = 1 (Huh7 cell line). I A schematic model of a feedback loop of PPP and PI3K/AKT signaling pathway inducing regorafenib-resistance in HCC.*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, mean ±SD