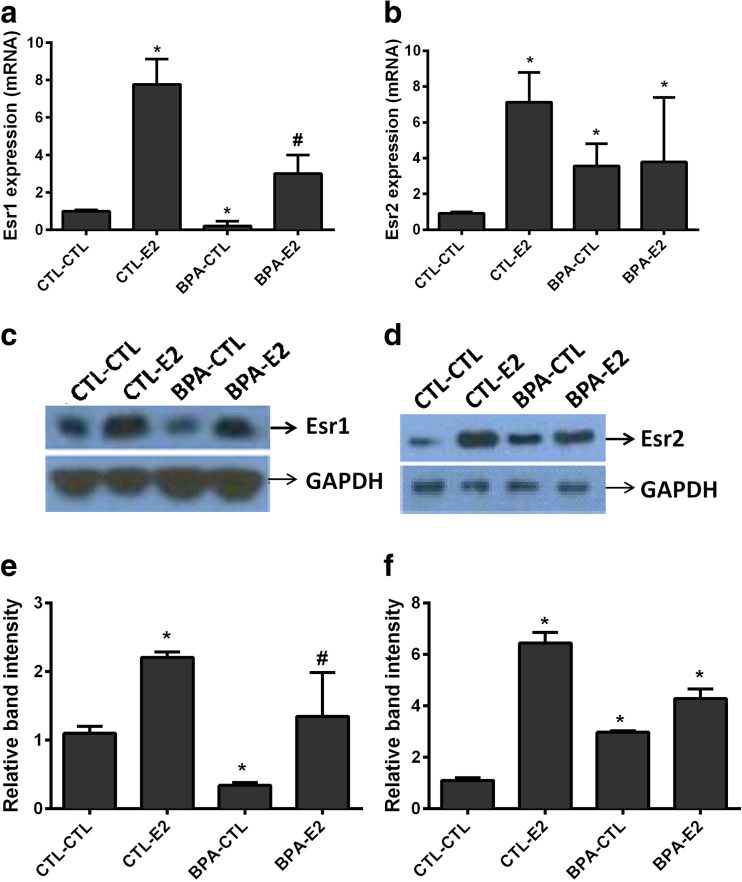
Fig. 4.
a–d Pre-natal exposure to BPA alters the expression of estrogen receptors Esr1 and Esr2 in mouse mammary gland. Results from qRT-PCR show the decreased expression of Esr1 (a) and increased Esr2 (b) mRNA levels in female offspring exposed to BPA in utero compared to controls. The Esr1 expression was increased after estrogen treatment in BPA-exposed mice while Esr2 expression was unchanged. Data represent the results obtained from four treatment groups. Mice exposed to BPA in utero were subsequently treated transiently with either E2 or sesame oil as vehicle control (CTL) as adults (BPA-CTL, BPA-E2). Similarly, animals exposed to vehicle in utero subsequently received transient E2 or vehicle control stimulation as adults (CTL-E2, CTL-CTL). The data are presented as relative mRNA expression in fold change relative to vehicle-treated controls (CTL-CTL). The bars in each graph represent the mean ± S.E. of three individual experiments, each performed in triplicate. *Denotes statistical significance (p < 0.05) compared to control group (CTL-CTL). #Denotes statistical significance (p < 0.05) compared to control group (CTL-CTL) and BPA exposed group (BPL-CTL). c, d The western blot analysis of Esr1 and Esr2, respectively. Protein (25 μg) from four treatment groups was subjected to 10 % SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted against anti-Esr1 and anti-Esr2 antibodies. The intensity of protein bands for Esr1 and Esr2 measured semi-quantitatively shown in e, f, respectively