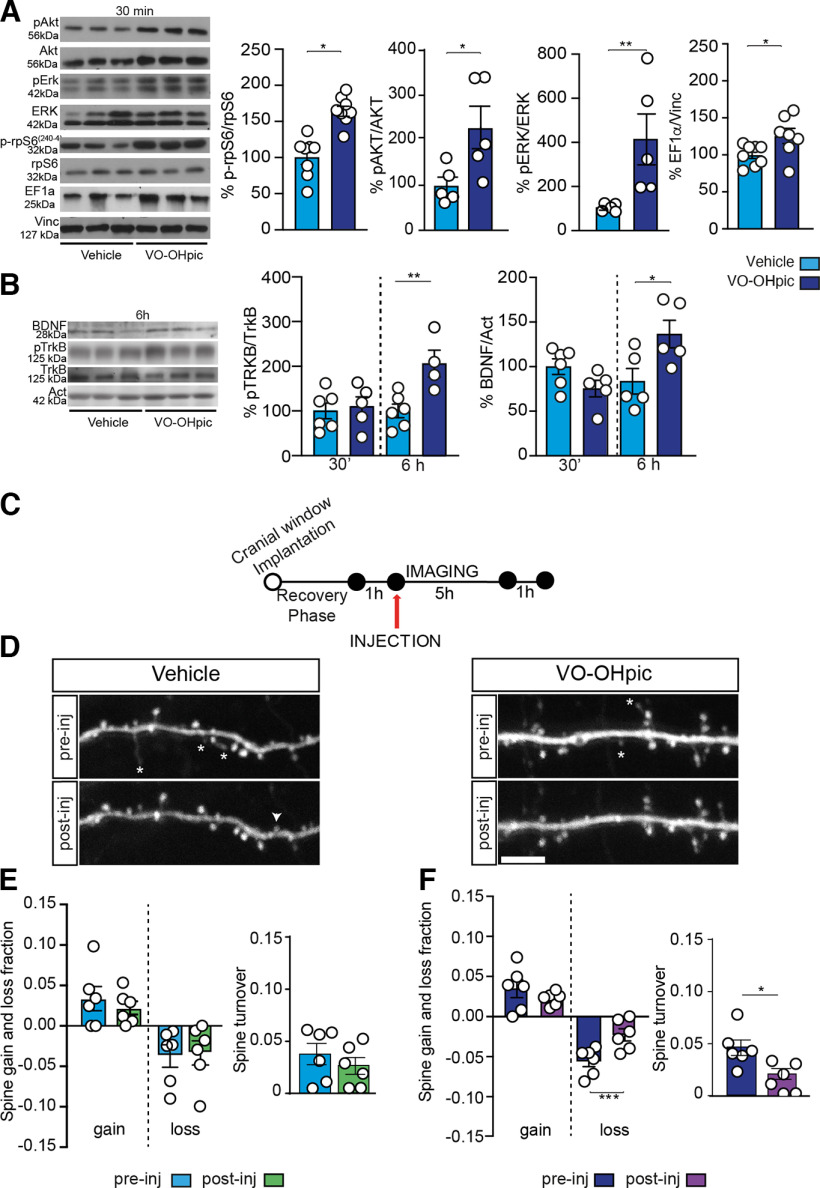
Figure 1.
PTEN inhibition with a single injection of VO-OHpic activates AKT/mTOR pathway and affects dendritic spines turnover. A, Representative Western blots of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway proteins. Quantitative analysis shows that AKT (Ser473), ERK (Thr 202/Tyr204), and rpS6 (SER240-4) phosphorylation as well as EF1α expression significantly increased in mouse forebrain 30 min after VO-OHpic injection. Vinculin was used as loading control. B, Representative Western blots of BDNF and pTrkB. Optical density analysis shows that both BDNF and pTrkB expression was unchanged 30 min after VO-OHpic treatment but almost doubled 6 h later. Actin was used as loading control. C, Two-photon imaging experimental design. D, Images of a dendritic branch from VO-OHpic and vehicle-treated mice before and after the injection. Asterisks indicate lost spines that were lost. Arrowheads point to gained spines through this period. E, F, VO-OHpic significantly affected spine turnover ratio. PTEN inhibition prevented the loss of immature spines compared (F) with vehicle-treated mice (E). Data are mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05. **p < 0.01. ***p < 0.001. Scale bar, 5 µm.