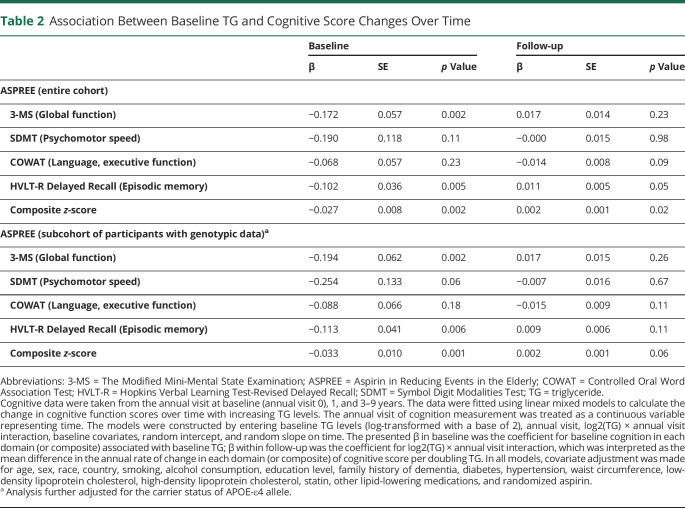
Table 2.
Association Between Baseline TG and Cognitive Score Changes Over Time
| Baseline | Follow-up | |||||
| β | SE | p Value | β | SE | p Value | |
| ASPREE (entire cohort) | ||||||
| 3-MS (Global function) | −0.172 | 0.057 | 0.002 | 0.017 | 0.014 | 0.23 |
| SDMT (Psychomotor speed) | −0.190 | 0.118 | 0.11 | −0.000 | 0.015 | 0.98 |
| COWAT (Language, executive function) | −0.068 | 0.057 | 0.23 | −0.014 | 0.008 | 0.09 |
| HVLT-R Delayed Recall (Episodic memory) | −0.102 | 0.036 | 0.005 | 0.011 | 0.005 | 0.05 |
| Composite z-score | −0.027 | 0.008 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.02 |
| ASPREE (subcohort of participants with genotypic data)a | ||||||
| 3-MS (Global function) | −0.194 | 0.062 | 0.002 | 0.017 | 0.015 | 0.26 |
| SDMT (Psychomotor speed) | −0.254 | 0.133 | 0.06 | −0.007 | 0.016 | 0.67 |
| COWAT (Language, executive function) | −0.088 | 0.066 | 0.18 | −0.015 | 0.009 | 0.11 |
| HVLT-R Delayed Recall (Episodic memory) | −0.113 | 0.041 | 0.006 | 0.009 | 0.006 | 0.11 |
| Composite z-score | −0.033 | 0.010 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.06 |
Abbreviations: 3-MS = The Modified Mini-Mental State Examination; ASPREE = Aspirin in Reducing Events in the Elderly; COWAT = Controlled Oral Word Association Test; HVLT-R = Hopkins Verbal Learning Test-Revised Delayed Recall; SDMT = Symbol Digit Modalities Test; TG = triglyceride.
Cognitive data were taken from the annual visit at baseline (annual visit 0), 1, and 3–9 years. The data were fitted using linear mixed models to calculate the change in cognitive function scores over time with increasing TG levels. The annual visit of cognition measurement was treated as a continuous variable representing time. The models were constructed by entering baseline TG levels (log-transformed with a base of 2), annual visit, log2(TG) × annual visit interaction, baseline covariates, random intercept, and random slope on time. The presented β in baseline was the coefficient for baseline cognition in each domain (or composite) associated with baseline TG; β within follow-up was the coefficient for log2(TG) × annual visit interaction, which was interpreted as the mean difference in the annual rate of change in each domain (or composite) of cognitive score per doubling TG. In all models, covariate adjustment was made for age, sex, race, country, smoking, alcohol consumption, education level, family history of dementia, diabetes, hypertension, waist circumference, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, statin, other lipid-lowering medications, and randomized aspirin.
Analysis further adjusted for the carrier status of APOE-ε4 allele.