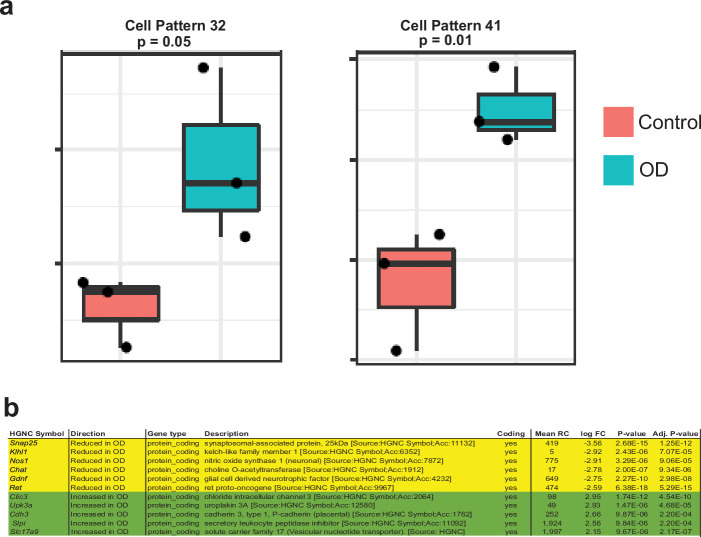
Figure 14. Patients with chronic gut dysmotility show significant shifts in their normal proportions of the two neuronal lineages.
(a) ProjectR-based projection of bulkRNAseq data from intestinal specimens of patients with normal motility and patients with obstructive defecation (OD), a chronic condition of intestinal dysmotility, into the 50 different NMF patterns learnt earlier, shows that the MEN-specific NMF patterns 32 and 41 were significantly upregulated in bulk-RNAseq of OD patients compared to controls. Data represent mean ± S.E.M. One-way ANOVA. Data mined from raw data generated by Kim et al., 2019 (b) OD patients show a significant decrease in the expression of important NENs-associated genes such as Ret, Gdnf, Snap-25, Nos1, Klhl1, and Chat, while showing a significant increase in the expression of important MENs-specific genes such as Clic3, Upk3a, Cdh3, Slpi, and Slc17a9. Data taken from Kim et al., 2019.