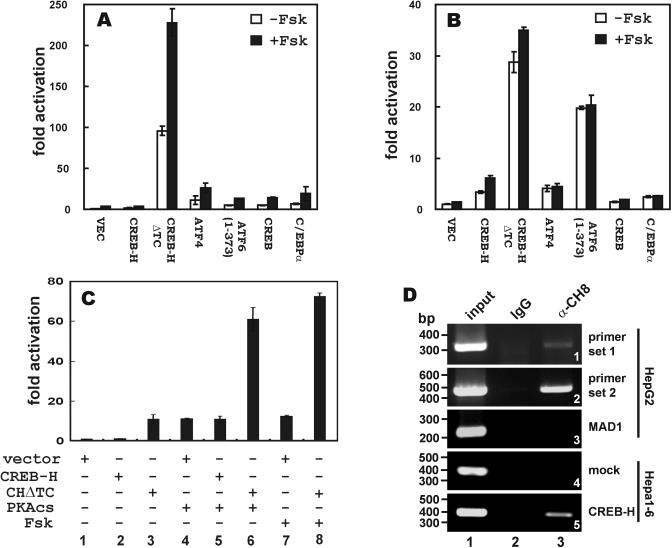
Figure 3.
Transcriptional activity of CREB-H and potentiation by cAMP. Empty vector (VEC) and plasmids (0.3 μg of each) expressing CREB-H, CREB-HΔTC (CHΔTC), ATF4, ATF6, CREB and C/EBPα were individually co-transfected with pCRE-Luc (A), pATF6-Luc (B) or pPEPCK-Luc (C) plasmid (0.2 μg) into HepG2 (A and B) and Hep3B (C) cells with or without the addition of Fsk or catalytic subunit of PKA (PKAcs). An SV40 promoter-driven Renilla luciferase plasmid was also transfected into the cells. The cell lysates were measured for Firefly luciferase luminescence and the readings were normalized by the luminescence of Renilla luciferase. (D) ChIP assay was performed with α-CH8 and extracts of HepG2 cells transfected with pcDNA-CREB-H. One control group received 10% of input chromatin (group 1). The other control group was given pre-immune IgG (group 2). Primer sets 1 and 2 were used to amplify sequences in the proximal promoter of human PEPCK gene (panels 1 and 2). Experiments were also carried out with primers for amplifying human MAD1 promoter (panel 3). Similar ChIP assays were performed in mock-transfected (panel 4) and CREB-H-expressing (panel 5) Hepa1-6 cells carrying a rat PEPCK promoter. Enforced expression of CREB-H was achieved by co-transfection with pcDNA-CREB-H. No CREB-H-bound DNA could be detected when input chromatin was omitted (data not down).