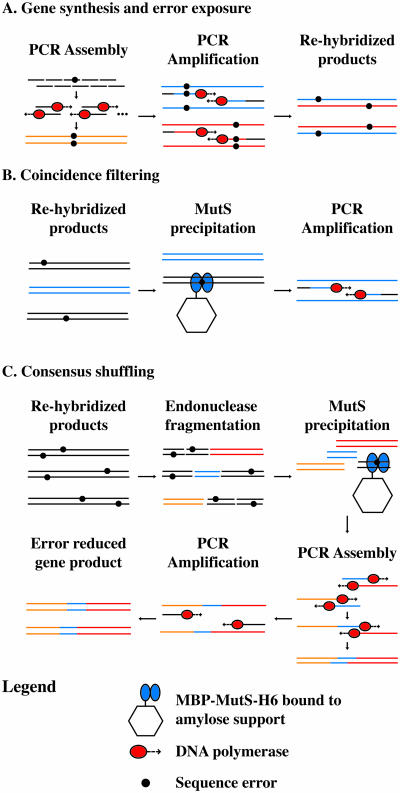
Figure 1.
Overview of gene synthesis, error exposure, coincidence filtering and consensus shuffling. (A) Gene synthesis from component oligonucleotides. PCR amplification of the PCR assembly reaction generates products that are re-hybridized to expose errors. Full-length genes: orange, blue and red lines. (B) Coincidence filtering on re-hybridized gene synthesis products containing few errors. Full-length genes containing errors are precipitated by MBP–MutS–H6 immobilized on amylose support. Error free gene: blue lines. (C) Consensus shuffling on re-hybridized gene synthesis products containing multiple errors. The re-hybridized gene synthesis products are fragmented, and error containing fragments are precipitated by MBP–MutS–H6 immobilized on amylose support. Error reduced fragments (orange, blue and red) are reassembled into the full-length gene followed by PCR amplification to generate error reduced products. Primers: black lines.