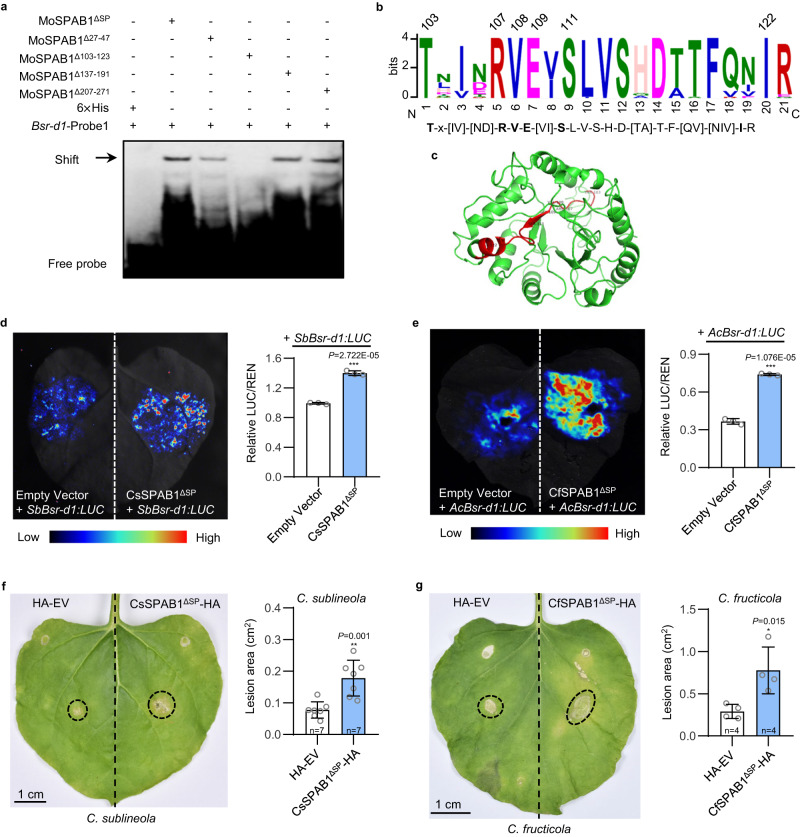
Fig. 4. Amino acids 103-123 of MoSPAB1 are required for binding to the Bsr-d1 promoter.
a Detection of MoSPAB1 domains required for binding to the conserved cis-element using EMSA. The regions of amino acids 27-47, 103-123, 137-191, and 207-271 of MoSPAB1ΔSP were deleted one by one, tagged with 6×His. Similar results are obtained from two independent biological experiments. b A LOGO sequence of the critical peptide (aa 103-123) of MoSPAB1. The conserved motif was predicted by aligning 45 homologous proteins using the MEME Suite. c A 3-D structure model for MoSPAB1 constructed by I-TASSER. The red portion represents the critical aa 103-123 region. Completely conserved amino acids are labeled. C-score = -1.61. Estimated TM-score = 0.52 ± 0.15. Estimated RMSD = 9.8 ± 4.6 Å. d Interaction of CsSPAB1ΔSP from Colletotrichum sublineola with the SbBsr-d1 promoter in luciferase activity assay using N. benthamiana leaves. Values are mean ± SD, n = 3 biologically independent samples. e Interaction of CfSPAB1ΔSP from Colletotrichum fructicola with the AcBsr-d1 promoter in luciferase assay using N. benthamiana leaves. f Transient expression of CsSPAB1ΔSP in N. benthamiana increases host susceptibility to C. sublineola. The pre-wounded Agrobacterium-infiltrated leaves were detached and inoculated with C. sublineola mycelial plugs after 24 hr post-infiltration. Lesion areas were denoted by circles, and scored 8 days post inoculation. Values are mean ± SD, n = 7 biologically independent samples. g Transient expression of CfSPAB1ΔSP in N. benthamiana increases host susceptibility to C. fructicola. Values are mean ± SD, n = 4 biologically independent samples. In (d–g) Data are analyzed by two-sided t-test, ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.