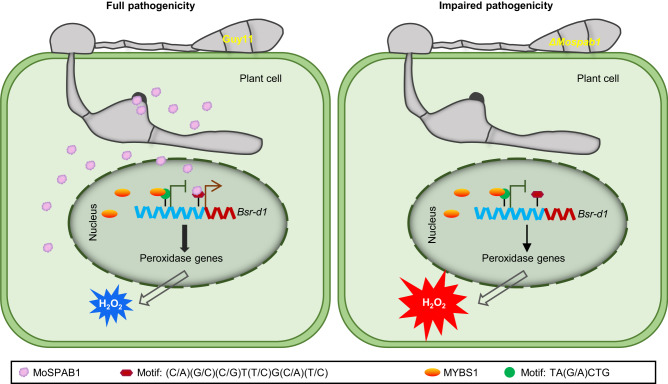
Fig. 5. A model for MoSPAB1-mediated pathogenicity.
During M. oryzae infection, MoSPAB1 was secreted from invasive hyphae and translocated to rice cytoplasm and the host nucleus. MoSPAB1 binds to the (C/A)(G/C)(C/G)T(T/C)G(C/A)(T/C) motif on the Bsr-d1 promoter and activates Bsr-d1. BSR-D1 accumulation accelerates H2O2 degradation by inducing expression of peroxidase genes, increasing disease susceptibility. Rice uses MYBS1 to suppress Bsr-d1 expression in order to combat M. oryzae MoSPAB1. Deletion of MoSPAB1 reduces M. oryzae pathogenicity on rice.