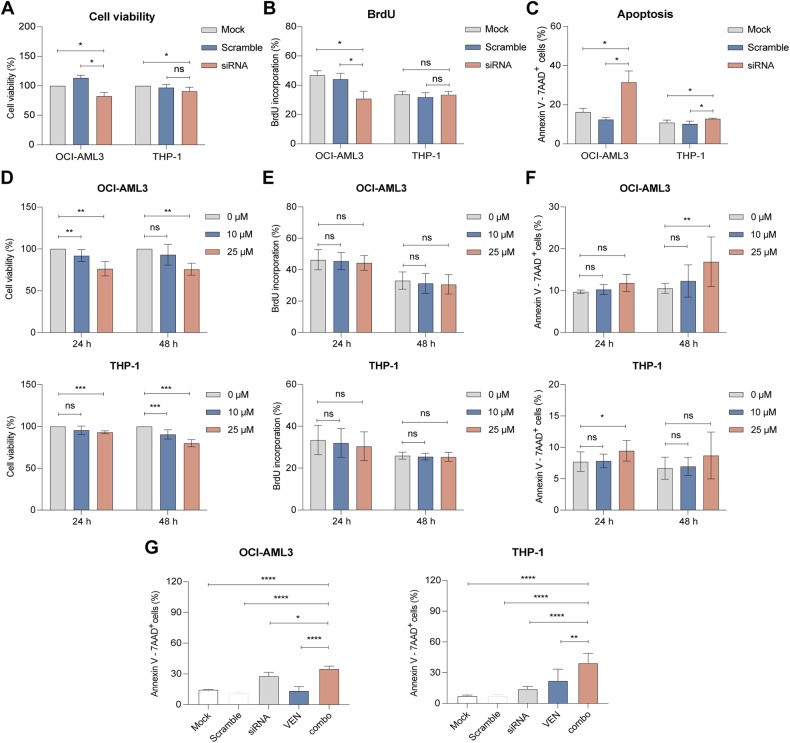
Fig. 6. Anti-leukemic effect of S100A9-siRNA and tasquinimod on cell viability, proliferation and apoptosis in venetoclax-resistant AML cell lines.
Venetoclax-insensitive OCI-AML3 and THP-1 cells were treated with 20 nM (OCI-AML3) or 60 nM (THP-1) S100A9-siRNA and Lipofectamine 2000. A mock (only lipofectamine) and scramble condition (negative control) were included as controls. A Cell viability was measured by CellTiter-Glo at 72 h (n = 4). B Cell proliferation was investigated using BrdU staining at 72 h (n = 4). C Apoptosis was measured using an AnnexinV 7-AAD staining and flow cytometry at 72 h (n = 3). D Cell viability of tasquinimod-treated OCI-AML3 and THP-1 cell lines (10 and 25 µM) was analyzed using a CellTiter-Glo assay after 24 and 48 h (n = 4). E Cell proliferation of tasquinimod-treated AML cells (10, 25 μM) was investigated using BrdU staining after 24 and 48 h (n = 4). F Apoptosis was measured using an AnnexinV 7-AAD staining and flow cytometry after 24 and 48 h (n = 4). G OCI-AML3 and THP-1 cells were pre-plated in RPMI medium with 10% fetal bovine serum in the presence or absence of S100A9-siRNA (20 nM) for 48 h and afterwards venetoclax (250 nM) was added for an additional 24 h. The Annexin-V/7-AAD based flow cytometric was used to determine the % of apoptotic cells. (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, One-way ANOVA, Error bars indicate SD).