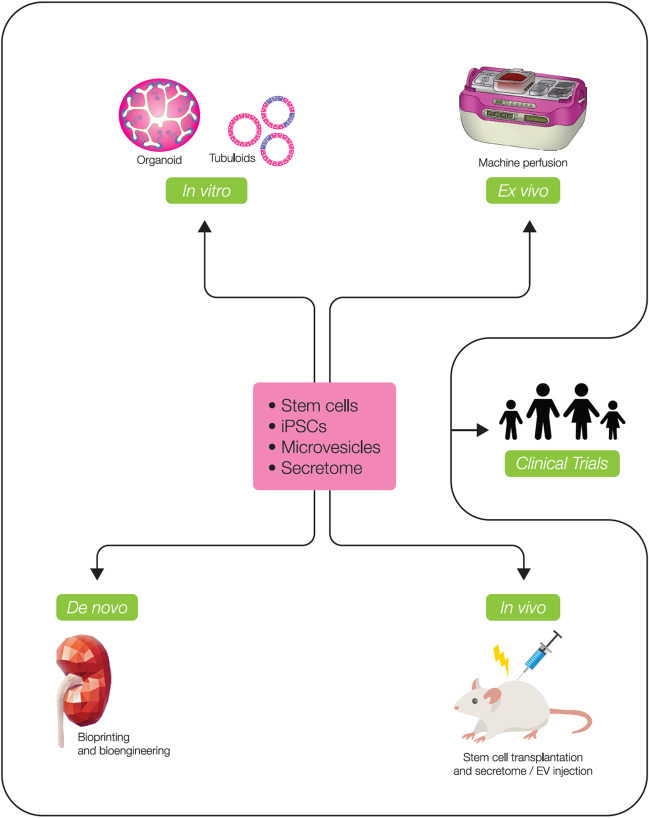
Fig. 2.
State-of-the-art tools applied in regenerative medicine approaches. In vitro: Kidney organoid cultures generated from iPSC can be used for modeling development, and together with tubuloids are valuable tools to model diseases and to test drugs. Additionally, iPSC-derived kidney organoids have potential to replace damaged kidney tissue. Ex vivo: Machine perfusion can serve as a suitable platform to locally boost the regenerative potential of donor kidneys having inferior quality prior to transplantation by means of cell therapy or drug injection. De novo: Bioprinting platforms can facilitate high throughput culture of highly consistent and reproducible organoid cultures to build kidney tissue. In vivo: Therapy including stem cell transplantations, cell secretome injection, and extracellular vesicles (EVs) injection can be used clinically to induce repair and regeneration, as already shown in pre-clinical models. All these methodologies are fundamental to elucidate the processes of kidney repair and regeneration prior to clinical trials and clinical applications