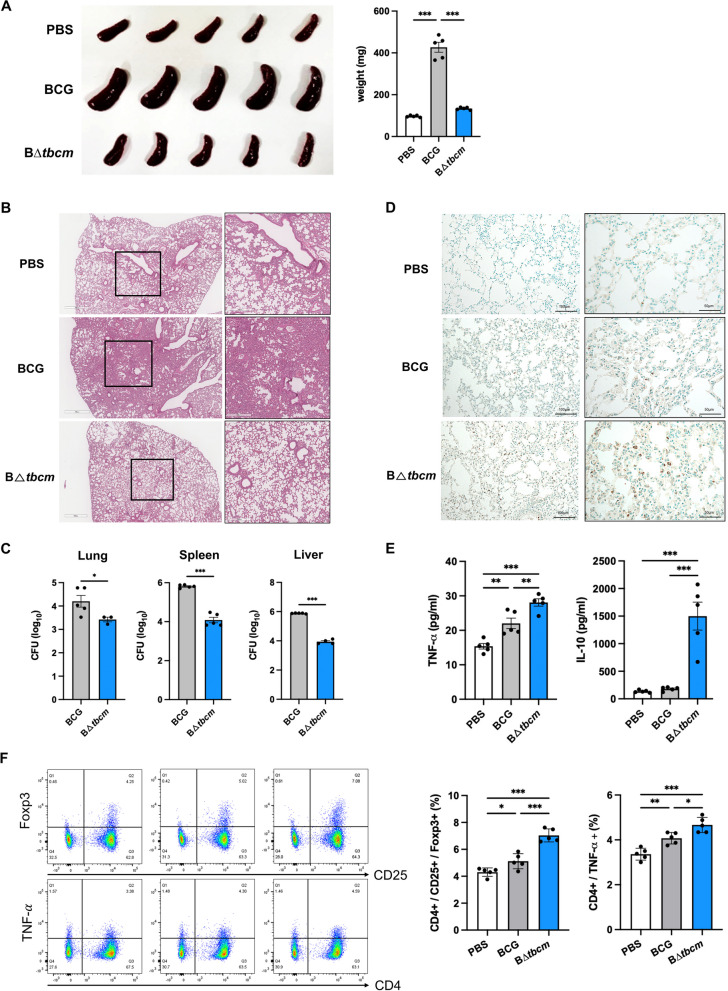
Fig. 2.
Deletion of tbcm enhances apoptosis in a mouse model. Female BALB/c mice (n = 5 per group) were infected with BCG or BΔtbcm (1 × 106 CFU) intravenously and sacrificed at 4 weeks postinfection. A Comparison of spleen size (left) and weight (right). B Histopathological images (H&E staining) of lung tissues (scale bars, 300 m or 700 m) C The bacterial burdens in lungs, spleens and livers were measured by the CFU assay. D Apoptotic cells in lung tissues were detected by the TUNEL assay (scale bars, 50 m or 100 m). E Splenocytes were isolated from infected mice and incubated for 3 days. The levels of TNF- and IL-10 were detected in the culture supernatants of splenocytes by ELISA.) CD25 + /Foxp3 + regulatory T cell and CD4 + /TNF-+ T-cell subsets were analyzed in splenocytes by flow cytometry. All data were collected in at least three independent experiments and are presented as the mean ± SEM. The results were analyzed for statistical significance by two-tailed Student’s t test (C) or one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test (A, E, F). (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). BCG, wild-type BCG; BΔtbcm, BCG Δtbcm mutant