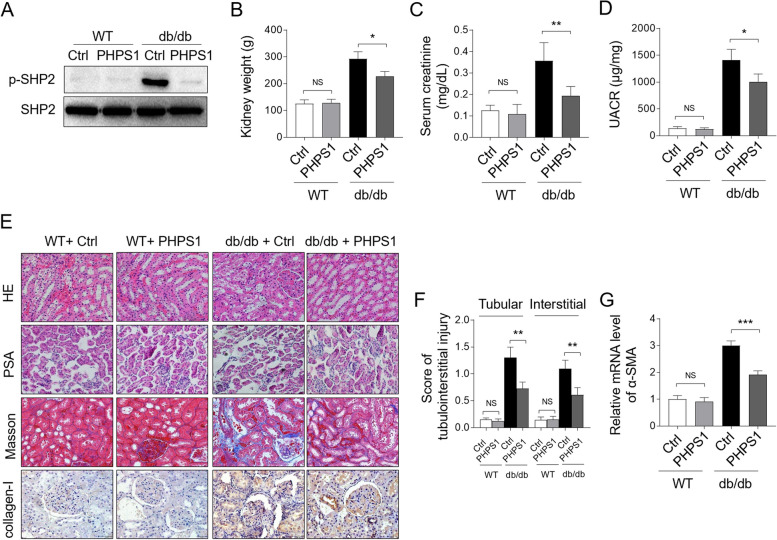
Fig. 3.
PHPS1 alleviates renal injury in db/db mice. A WT and db/db mice were adminstrated i.p. with 8 mg/kg/d PHPS1 for 12 weeks, starting at 8 weeks to 20 weeks of age. Injecton of equal volume of vehicle was used as control (Ctrl). Each group included 6 mice. The levels of p-SHP2 and basal SHP2 protein were determined by Western blot analysis. B-D Mice were treated as in (A). Mouse kidneys in each group were harvested and weighted (B). The urinary albumin and creatinine levels were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and the serum creatinine level (C) and urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR) (D) were presented. Student’s test, *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; NS, not significant (n = 6). E Histologic examinations of renal sections from each group were performed via hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining and periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining. Masson trichrome staining and IHC staining of collagen-I were employed to measure collagen fiber deposition. F The tubulointerstitial injury in (E) was semiquantified and the score in each group was depicted. Student’s test, **, p < 0.01; NS, not significant (n = 6). G The mRNA level of α-SMA in renal tissue was detected by qRT-PCR analysis. Student’s test, ***, p < 0.001; NS, not significant (n = 6)