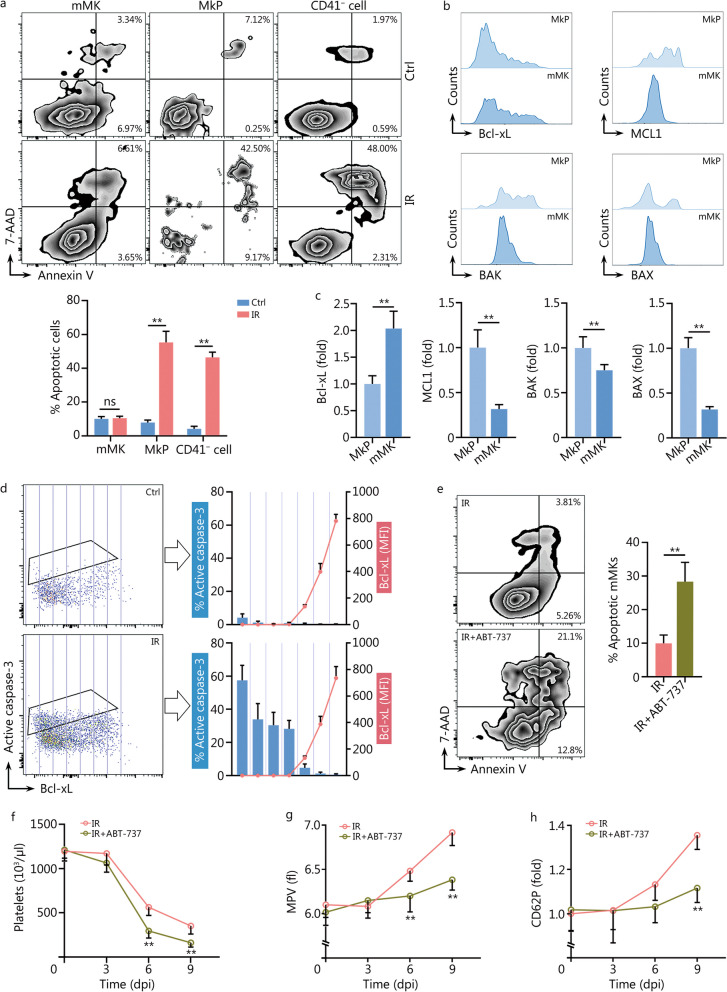
Fig. 3.
The inherently high pro-survival threshold confers radioresistance onto mMKs. a Flow cytometric analysis and quantification of MK and non-MK apoptosis in BM of mice at 1 dpi (n = 5). b, c Flow cytometric analysis and quantification of pro-survival (Bcl-xL and MCL1) and pro-apoptotic (BAX and BAK) Bcl-2 family protein expression in BM MKs of mice (n = 5). d Flow cytometric analysis and quantification of the relationship between Bcl-xL expression and apoptosis as reflected by active caspase-3 expression in BM CD41+ MKs of mice at 1 dpi (n = 5). e Flow cytometric analysis and quantification of mMK apoptosis in BM of mice with or without ABT-737 treatment at 1 dpi (n = 5). Platelet counts (f) and MPV (g) in peripheral blood of mice with or without ABT-737 treatment at indicated dpi (n = 6). h CD62P expression in response to thrombin on washed platelets from mice with or without ABT-737 treatment at indicated dpi (n = 5). Data represent mean ± standard deviation. **P < 0.01, compared to Ctrl, MkP or IR as indicated. Two-tailed unpaired student’s t-test. ns non-significance, MK megakaryocyte, mMK mature MK, MkP MK progenitor, Ctrl control, IR ionizing radiation, dpi day post IR, 7-AAD 7-amino-actinomycin D, MFI mean fluorescence intensity, BM bone marrow, MPV mean platelet volume