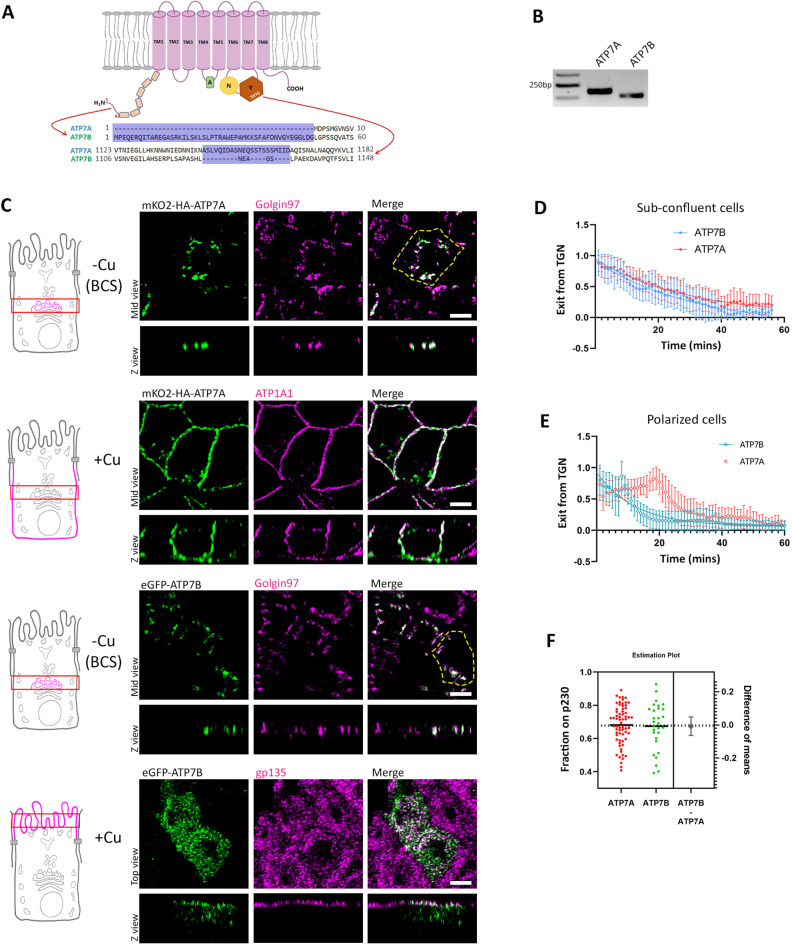
Fig. 1.
ATP7A and ATP7B are homologous proteins and are expressed in MDCK cells but traffic to different surfaces in response to copper. (A) Illustration showing the structure of the Cu-ATPases with major sequence differences between ATPA and ATP7B drawn out. (B) Transcript levels of dog ATP7A and ATP7B showing the expression of both the transporters in MDCK cells. Gel representative of three repeats. (C) Polarized MDCK cells showing localization of transfected mKO2–HA–ATP7A and eGFP–ATP7B in copper-depleted and copper-treated conditions. Under copper-depleted conditions, both proteins localize at the TGN marked by golgin-97. Upon copper treatment, ATP7A traffics to the basolateral surface (marked by ATP1A1) and ATP7B traffics to the apical surface (marked by gp135). The yellow dashed line indicates the cell boundary. (D) Fitted curve of decreased pixel count for both the Cu-ATPases, mKO2–HA–ATP7A and eGFP–ATP7B, in response to copper in sub-confluent MDCK cells revealing similar dispersion and Golgi-exit rates. Sample size (N) for ATP7A: 20, ATP7B: 13. (E) Fitted curve of decreased pixel count of both the Cu-ATPases, mKO2–HA–ATP7A and eGFP–ATP7B, in response to copper in polarized MDCK cells. Sample size (N) for ATP7A: 20, ATP7B: 25. (F) Colocalization quantification (Manders’ colocalization coefficient) for transfected mKO2–HA–ATP7A and eGFP–ATP7B with the TGN marker p230 (Fixed cells treated with 2.5 µM CuCl2 for 30 min) reveals their equal sensitivity to copper. Results in D–F are mean±s.d. Scale bars: 5 µm.