Fig. 6.
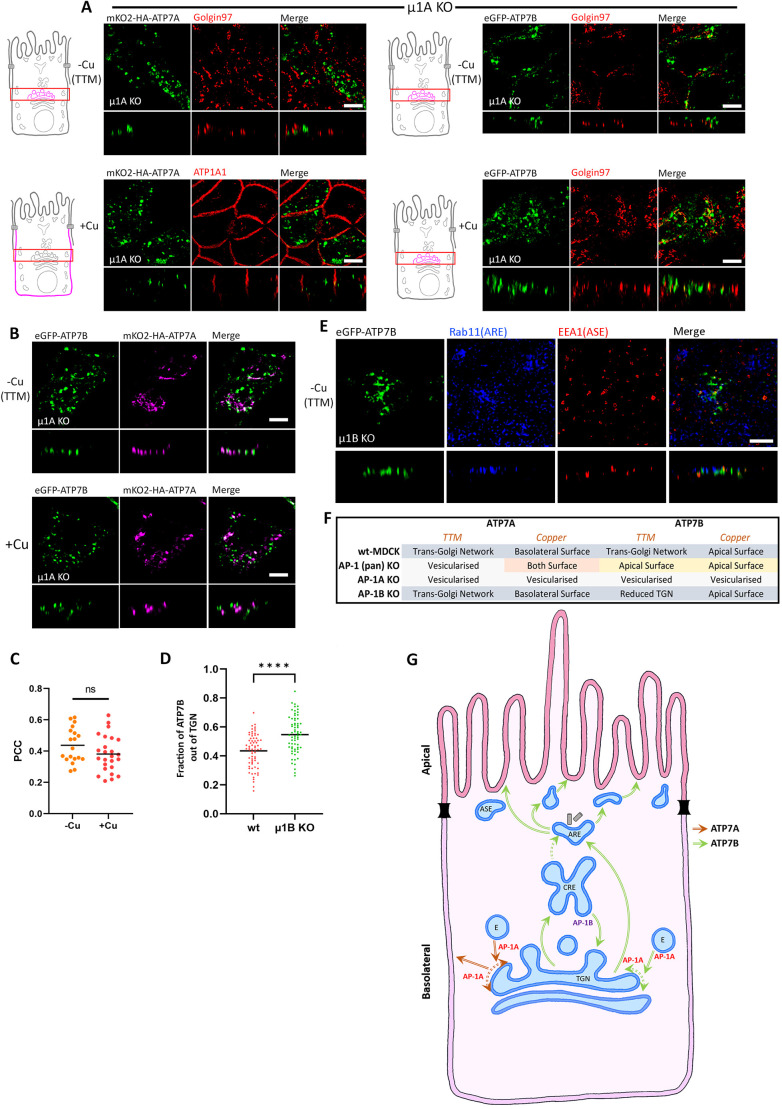
AP-1A is crucial for TGN retention as well as copper-mediated trafficking. (A) Images showing localization of ATP7A and ATP7B in polarized AP-1A KO MDCK cells (i.e. µ1A KO cells) in copper-deprived and elevated conditions. Both the Cu-ATPases lost their TGN localization and were found vesicularized in both the copper levels and failed to reach the plasma membrane, which indicates the crucial role of AP-1A in copper-mediated trafficking. (B) Images showing localization of mKO2–HA–ATP7A and eGFP–ATP7B co-transfected in polarized AP-1A KO MDCK cells (i.e. µ1A KO cells) in copper-deprived and elevated conditions. Both ATP7A and ATP7B localize to different endosomal compartments with minimal overlap. (C) Colocalization quantification (Pearson's correlation coefficient) of transfected mKO2–HA–ATP7A with eGFP–ATP7B from B. This shows that there is no effect of copper on the localization of ATP7A and ATP7B in AP-1A KO cells. Line is mean (n=−Cu, 19; +Cu, 25). (D) Fraction of transfected eGFP–ATP7B located outside of the TGN marked by golgin-97 (calculated by 1 – Manders' colocalization coefficient) in TTM-treated wild-type (wt) and AP-1B KO MDCK cells. An increased fraction of ATP7B in µ1B KO cells compared to in wild-type cells shows the role of AP-1B in copper-independent recycling. Line is mean (n=wt, 68; µ1B KO, 66). (E) Confocal images showing ATP7B in polarized AP-1B KO MDCK cells under copper-chelated conditions. Absence of ATP7B (green) in Rab11-positive (blue) and EEA1-positive (red) compartments suggests lack of anterograde trafficking or spillover from CREs due to regulation by AP-1B in basolateral trafficking at CREs. Images representative of at least three repeats. (F) Tabulated summary of trafficking phenotypes of ATP7A and ATP7B in AP-1A KO, AP-1B KO and AP-1 (pan) KO MDCK cells. (G) Proposed model for copper-independent and copper-dependent trafficking of both the Copper ATPases, i.e., ATP7A and ATP7B, in polarized MDCK cells. Common endosomal stations are marked, like the TGN, CREs, AREs, ASEs and endosomes (labeled with an E). Red arrows mark the trafficking itinerary of ATP7A and the green arrows represents the trafficking path of ATP7B. The dotted green arrow denotes a possible movement of endocytosed cargoes from CREs to the AREs. Dotted double headed arrows denote possible TGN retention by AP-1A. Scale bars: 5 µm.