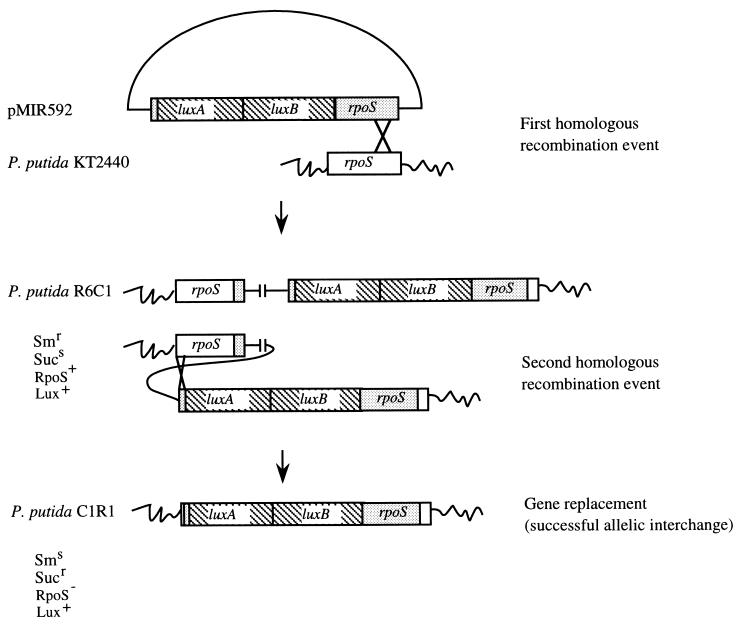
FIG. 3.
Replacements of the rpoS gene with the luxAB insertion mutant rpoS gene. A single homologous recombination event between the functional rpoS present on the chromosome of P. putida KT2440 and the inactivated rpoS present on pMIR592 was isolated by selection for resistance to streptomycin (pMIR592 [Fig. 1]). One of the Smr (see the footnote to Table 1 for abbreviations) transconjugants was selected and named R6C1; this merodiploid strain contained the entire plasmid pMIR592 integrated in the genome. A second crossover event at the rpoS locus was selected by cultivating R6C1 overnight in LB without streptomycin (about 10 generations) and subsequent plating on LB medium supplemented with 10% sucrose. Sucr colonies were analyzed by replica plating. One of the Sucr Sms Lux+ colonies was called C1R1. The genomes of three merodiploid isolates (from three independent matings) obtained as the result of the first recombination event and the genomes of six clones (two from each merodiploid) obtained as the result of the resolution of the merodiploids after the second recombination event were examined by Southern blot analysis, which revealed correct single and double recombination events, respectively, at the rpoS locus (not shown).