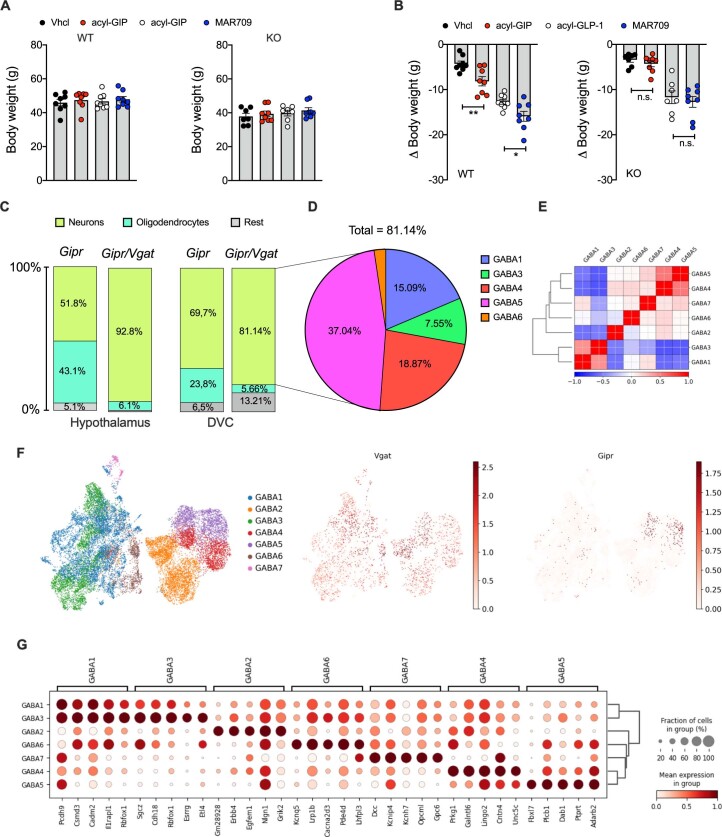
Extended Data Fig. 6. Effects of acyl-GIP, acyl-GLP-1 and MAR709 on absolute body weight in HFD-fed Vgat-Gipr KO mice, and analysis of Vgat/Gipr in published scRNA repositories.
Starting body weight (a) and body weight change (b) in 38-wk old male C57BL/6J wild-type (WT) or Vgat-Gipr KO mice treated daily with either Vehicle, acyl-GIP (100 nmolkg), or 10 nmol/kg of either acyl-GLP-1 or MAR709 (n = 7-8 each group). Cell types expressing Vgat and/or Gipr in the hypothalamus and dorsal vagal complex (DVC) (c). Distribution of cells co-expressing Gipr and Vgat within 7 clusters of GABAergic neurons identified in the DVC (d). Correlation plots with Pearson’s correlations between 7 clusters (GABA1-7) of GABAergic neurons in the DVC (e). UMAP of GABAergic neurons in the DVC colored by GABAergic neuron cluster, and expression of Vgat and Gipr in each cell, with the color corresponding to log-normalized UMI counts scaled to the maximum of each gene (f). The dot plot of the top 5 genes most associated with each GABAergic neuron population as determined by Wilcoxon-rank-sum test (g). Data in panel A were analyzed using ordinary 1-way ANOVA, data in panel B were analyzed using ordinary 1-way ANOVA and using Holm-Sidak multiple comparison test. Date represent means ± SEM; asterisks indicate * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01 and *** p < 0.001. Individual p values are shown in the Data Source file, unless p < 0.0001. Data shown in panels C, D, E, F, G were generated based on publicly available snRNA Seq datasets of hypothalamus (Steuernagel et al.15) or DVC (Lugwig et al.17).