Fig. 2.
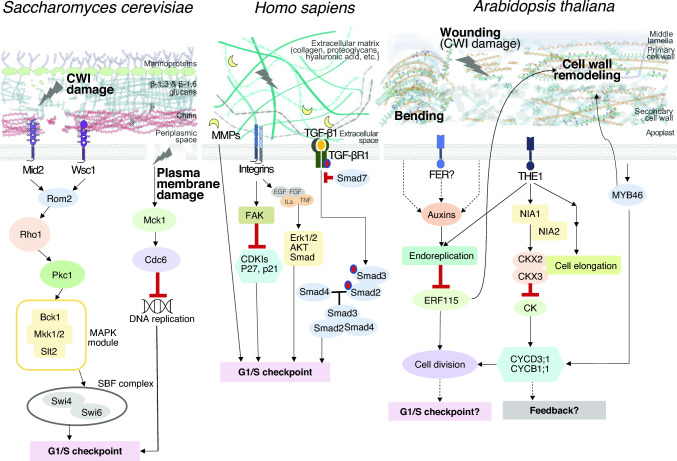
Pathways controlling cell cycle progression in function of the integrity of the cell wall or extracellular matrix are similar in different eukaryotes. In the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisae, CWI and plasma membrane damage initiate downstream responses, culminating in a G1/S cell cycle arrest, with receptors Mid2 and Wsc1 playing key roles in damage detection. Similarly, in humans such as Homo sapiens, damage to the extracellular matrix is detected by integrins, which trigger comparable transduction cascades resulting in G1/S cell cycle arrest, a process also elicited by extracellular matrix modifications via metalloproteinases (MMPs). The TGF-β pathway also control cell proliferation, regulating ECM synthesis and degradation, and modulating tissue remodeling processes. Integrins, as primary receptors for ECM proteins, establish bidirectional communication with growth factor and cytokine receptors. In plants like Arabidopsis thaliana, varied pathways respond to folding and wounding, influencing cell elongation or division and prompting cell wall remodeling, detected by THESEUS1 (THE1). FERONIA (FER) could also play a role due to its effect on auxin concentrations, however, while implied, the explicit link to the cell cycle checkpoint remains to be confirmed (dotted lines)