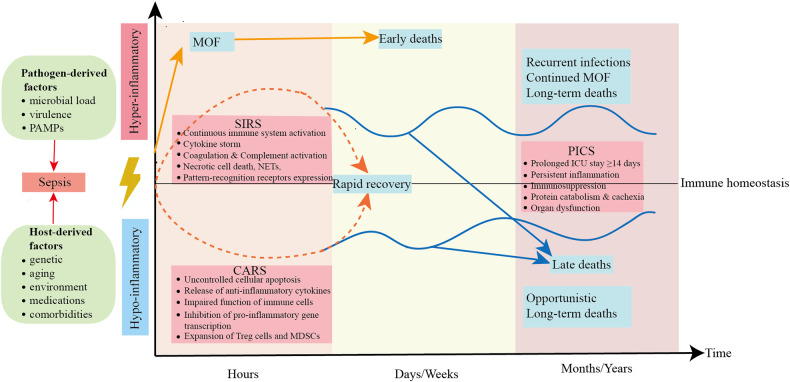
Fig. 1. Host immune response in sepsis.
Activation of both proinflammatory and anti‐inflammatory immune responses occurs promptly after sepsis onset. The host response to severe sepsis can have four different clinical trajectories: (1) early MOF leading to death, (2) rapid recovery, (3) late deaths, or (4) late sequelae or long-term deaths. SIRS, systemic inflammatory response syndrome; CARS compensatory anti‐inflammatory response syndrome, MOF multi-organ failure, NETs Neutrophil extracellular traps, MDSCs Myeloid-derived suppressor cells, ICU intensive care unit, PICS persistent inflammation, immunosuppression, and catabolism syndrome.