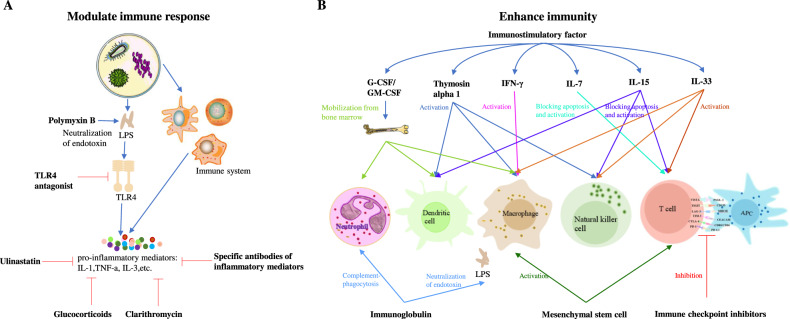
Fig. 3. Potential immunotherapy for patients with sepsis-modulate the immune responses or enhance immunity.
A Modulate immune responses that provoke excessive inflammation during sepsis. B Enhance immunity during sepsis. The immune response in sepsis is a highly individualized process. Sepsis patients’ immune responses vary depending on their immunological condition at the time of infection, age, comorbidities, environmental variables, and microbiome. Precise immunotherapy can significantly improve the prognosis of sepsis. LPS lipopolysaccharide, TLR4 toll like receptor 4, IL interleukin, TNF-α tumor necrosis factor-alpha, G-CSF Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, GM-CSF granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor, IFN-γ interferon-gamma, APC antigen-presenting cell.