Fig. 3.
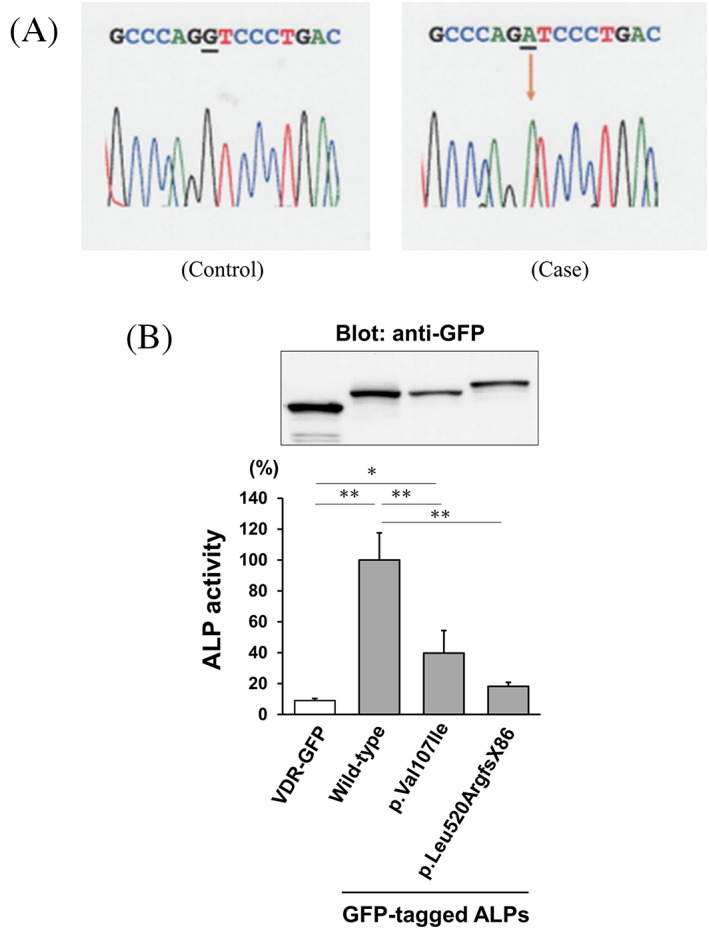
(A) The novel variant of the ALPL gene in the current case. Sanger sequencing identified a homozygous missense variant in exon 5 of the ALPL gene (c.319G > A; p.Val107Ile). (B) The bar graph shows the mean with standard deviation of the enzymatic activity. The p.Val107Ile variant of TNSALP was decreased to approximately 40% of the wild type. As a negative control, a fusion protein of vitamin D receptor and GFP (VDR‐GFP) was introduced. For comparison, the p.Leu520ArgfsX86 (c.1559delT) variant of TNSALP, which is the most prevalent variant in the Japanese population, was coassayed. The enzymatic activity was normalized based on the signal intensity in Western blotting using aliquots of the cell lysates and an anti‐GFP antibody. The enzymatic activity in the cells expressing wild‐type TNSALP was designated as 100%. Data are shown as the mean ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 using one‐way ANOVA with the Tukey–Kramer test.
