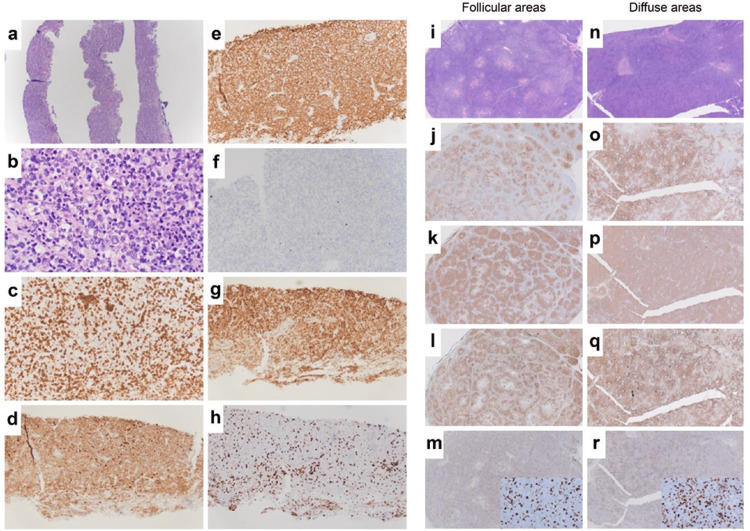
Figure 1. Surgical pathology.
Core needle biopsy (a–h) and excisional axillary lymph node biopsy (i–r). i–m of the excisional lymph node biopsy demonstrates a histologic pattern consistent with follicular lymphoma, while n–r of the excisional lymph node biopsy demonstrates a histologic pattern consistent with the diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). (a) 4x and (b) 50x H&E; (c) 20x CD3 stains reactive infiltrating T cells; (d) 20x CD10 stains B cells of follicle center origin (including lymphoma cells in follicular lymphoma and DLBCL); (e) 20x cd20+, marker for B lymphocytes; (f) 20x CD21+, marker for follicular dendritic cells; (g) 20x BCL-2, an anti-apoptotic protein detected in follicular lymphomas and associated with BCL-2 overexpression due to t(14;18) translocations; (h) 20x Ki-67, marker of cell proliferation; (i) 2x H&E follicular areas; (j) 2x CD10+; (k) 2x CD20+; (l) 2x BCL-2; (m) 2x (insert 40x) Ki-67; (n) 2x H&E diffuse large B cell; (o) 2x CD10+; (p) 2x CD20+; (q) 2x BCL-2; (r) 2x (insert 40x) Ki-67.