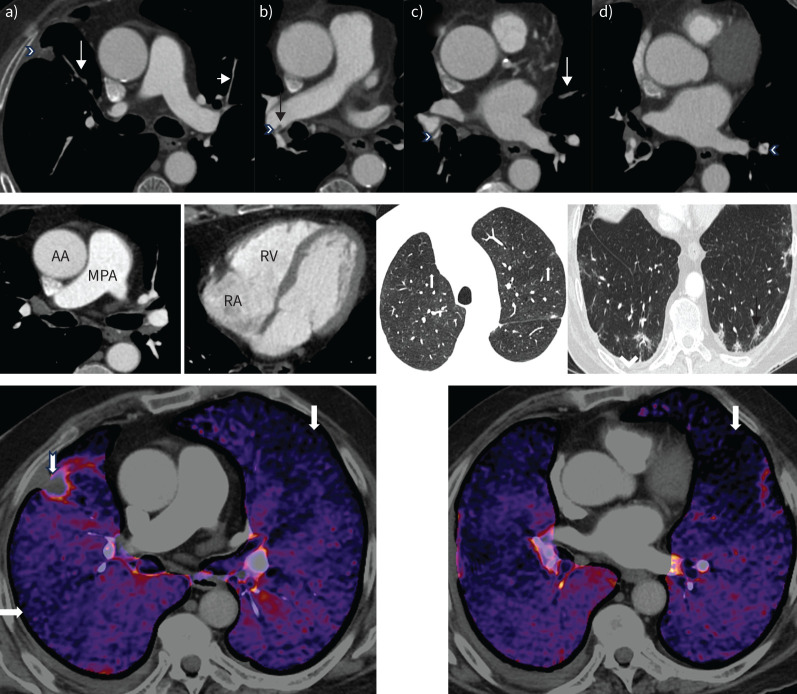
FIGURE 2.
Computed tomography (CT) pulmonary angiography of patient 1. Upper panel: axial views. a) Occluded anterior segment of right upper lobe (long arrow) with a small peripheral infarct (arrowhead). The anterior segment of the left upper lobe is very attenuated (short arrow). b) Intravascular shelf in the right interlobar artery (arrow) and stenosis at the origin of the right lower lobe vessel (arrowhead). c) Segmental web in the right lower lobe (arrowhead) and occluded segmental lingula (arrow). d) Segmental web in the left lower lobe (arrowhead). Middle panel: mediastinal windows showing a normal calibre main pulmonary artery (MPA) and an MPA/ascending aorta (AA) ratio <1.0. The right atrium (RA) and right ventricle (RV) are not dilated. There is no right ventricular hypertrophy. Lung windows demonstrate mosaic attenuation (left, white arrows point to poorly perfused regions), peripheral infarct (right, black arrow) and a small right pleural effusion (arrowhead). Lower panel: dual-energy CT pulmonary angiography demonstrates multiple segmental perfusion defects in both lungs (arrows). There is a small peripheral pulmonary infarct in the right upper lobe (notched arrow).