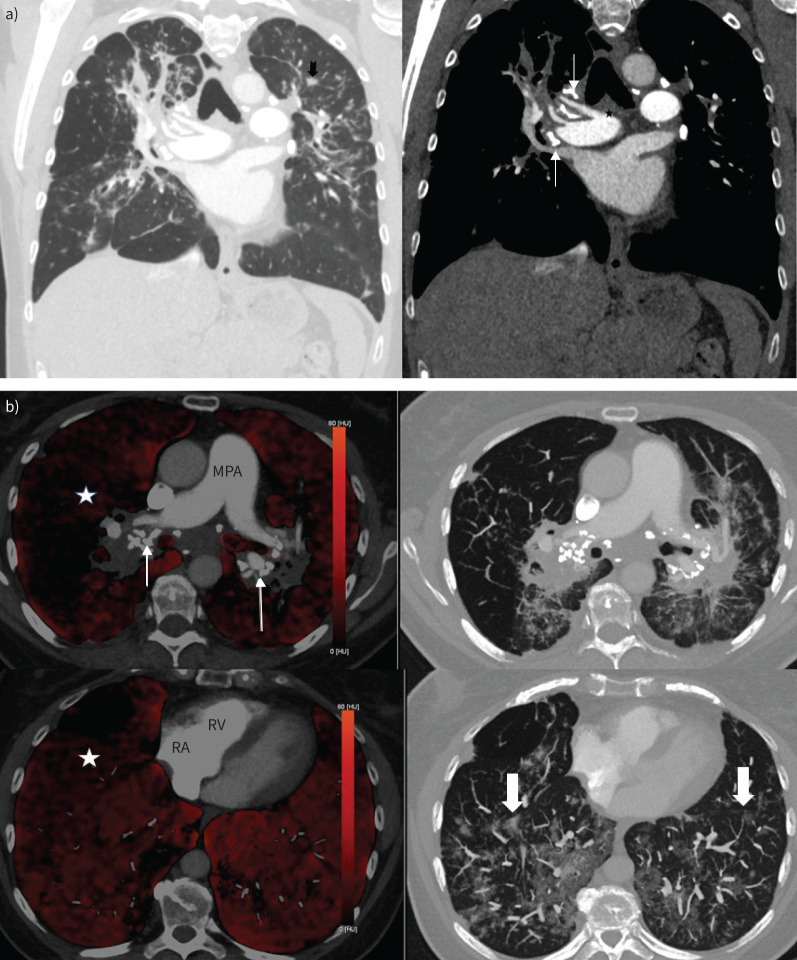
FIGURE 2.
a) Coronal view computed tomography pulmonary angiography (CTPA) (left panel: lung window; right panel: mediastinal window). There is bilateral upper zone predominant pulmonary fibrosis with ill-defined centrilobular nodules (notched black arrow) and calcified mediastinal and hilar lymph nodes (thin white arrows). The main pulmonary artery (star) was nondilated. b) Axial dual-energy CTPA images demonstrating heterogenous reduction of perfusion in the right lung (white star) on iodine maps (left panel) with markedly calcified bilar hilar lymphadenopathy (thin arrows). There are few centrilobular ground glass opacities (block arrows) in the lower zones (right panel). Of note, the main pulmonary artery (MPA) is not particularly dilated and there is no right-sided cardiac chamber enlargement. RA: right atrium; RV: right ventricle.