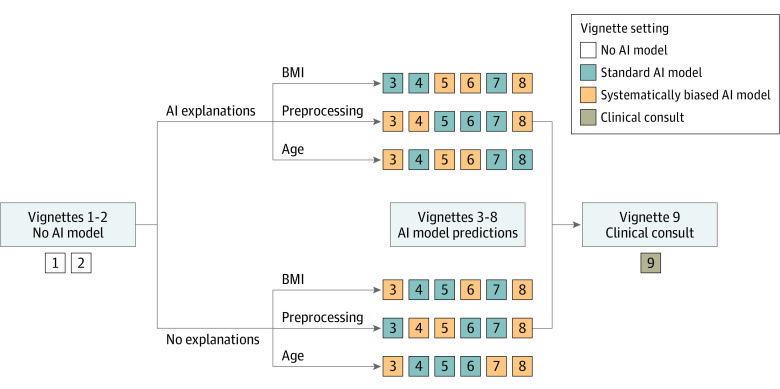
Figure 1. Randomization and Study Flow Diagram for the 9 Clinical Vignettes.
After completing informed consent, participants were randomized to artificial intelligence (AI) predictions with or without explanations and all participants were also randomized to 1 of 3 types of systematically biased AI models during a subset of vignettes in the study. The 3 systematically biased AI models included a model predicting pneumonia if aged 80 years or older, a model predicting heart failure if body mass index (BMI, calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared) was 30 or higher, and a model predicting chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) if a blur was applied to the radiograph. Participants were first shown 2 vignettes without AI predictions to measure baseline diagnostic accuracy. The next 6 vignettes included AI predictions. If the participant was randomized to see AI explanations, the participant was also shown an AI model explanation with the AI predictions. Three vignettes had standard AI predictions, and 3 had biased AI predictions shown in random order. The final vignette included a clinical consultation, a short narrative provided by a hypothetical trusted colleague who identified the correct diagnosis and their diagnostic rationale.