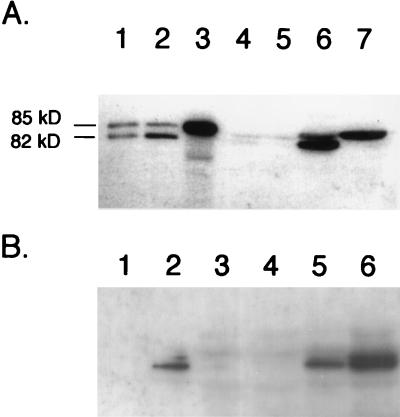
FIG. 2.
Analysis of polypeptides induced by the presence of plasmid pMU10 and which cross-react with anti-E. coli PFL antibodies. Crude extracts from various E. coli strains were separated in 7.5% (wt/vol) polyacrylamide gels according to the method of Laemmli (19), and after transfer to nitrocellulose membranes, the polypeptides were challenged with anti-E. coli PFL antibodies. (A) Influence of a mutation in the gene encoding PFL-activating enzyme on migration of cross-reacting polypeptides. The positions of the intact PFL polypeptide (85 kDa) and the specific fragmentation product (82 kDa), derived from exposure of the radical form of the enzyme to oxygen, are shown. Lane 1, MC4100 (wild type) grown aerobically (100 μg of protein); lane 2, MC4100 grown anaerobically (7.5 μg of protein); lane 3, 234M11 grown anaerobically (7.5 μg of protein); lane 4, RM202 (Δpfl)/pBR322 grown anaerobically (150 μg of protein); lane 5, RM221 (Δpfl Δact)/pBR322 grown anaerobically (150 μg of protein); lane 6, RM202/pMU10 grown anaerobically (150 μg of protein); lane 7, RM221/pMU10 grown anaerobically (150 μg of protein). (B) Western blot demonstrating that induction of TdcE synthesis by pMU10 occurs anaerobically. Lane 1, MC4100 grown aerobically (7.5 μg of protein); lane 2, MC4100 grown anaerobically (7.5 μg of protein); lane 3, RM202 (Δpfl)/pBR322 grown aerobically (100 μg of protein); lane 4, RM202/pBR322 grown anaerobically (100 μg of protein); lane 5, RM202/pMU10 grown aerobically (100 μg of protein); lane 6, RM202/pMU10 grown anaerobically (100 μg of protein).