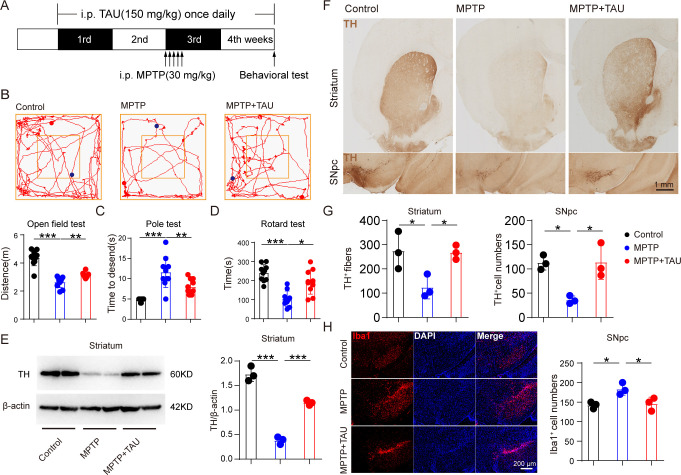
Fig 7.
Taurine administration prevented motor deficits, DA neuronal loss, and microglial activation in MPTP-treated mice. Male C57BL/6 mice were domesticated for 7 days then were treated with 200-µL saline containing taurine (150 mg/kg) or 200-µL saline via intraperitoneal injection every day for 4 consecutive weeks. Two hundred-microliter saline containing MPTP (30 mg/kg) or 200-µL saline via intraperitoneal injection every day for a total of five times, starting from day 15. On day 28, behavioral tests were performed to evaluate the motor function, and the mice were sacrificed to determine the pathology of mice by immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, and immunoblot. (A) The experimental flowchart. (B) Representative traces in the open field test and quantification of performance in the open field test. Blue points: starting positions; red points: ending positions (n = 10). (C and D) Quantification of performance in the pole test and the rotarod test (n = 10). (E) Representative bands of TH protein in the striatum of one hemisphere determined by WB and quantification of TH expression (n = 3). (F and G) Representative immunohistochemistry images and quantification of TH-positive fibers and neurons in striatum and SNpc (n = 3). (H) Representative immunofluorescence images and quantification of Iba1-positive cells (n = 3). Data are expressed as mean ± SD, and representative results are one of three independent experiments. All statistical differences were tested using one-way analysis of variance. Quantification of TH-positive fibers and neurons and Iba1-positive cells was performed by ImageJ. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.