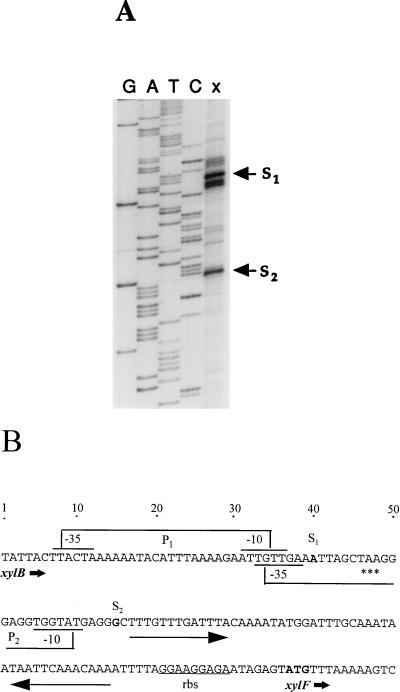
FIG. 3.
Identification of xylF transcript initiation and putative regulatory sequences. (A) Primer extension analysis. The end-labelled primer (5 × 105 cpm) was annealed to RNA (40 μg) from T. ethanolicus grown on 0.4% xylose and was extended with reverse transcriptase. An aliquot from the primer extension reaction (lane x) was electrophoresed on a denaturing 8% polyacrylamide gel along with the sequence ladder generated with the same oligonucleotide (lanes G, A, T, and C). The two cDNA products representing major transcript initiation sites (S1 and S2) are marked. (B) Regulatory elements of xylAB and xylF. A portion of the sequence including the xylB 3′ end, xylB-xylF intercistronic spacer, and xylF 5′ terminus is shown along with transcriptional and translational signals. P1 and P2 indicate the upstream and downstream xylF promoters, respectively. Long arrows depict a palindromic sequence possibly serving as the xylAB transcriptional terminator and the xylF operator (see Discussion). The potential transcription and translation start sites are shown in boldface. rbs, ribosome-binding sequence; asterisks, translation termination codon of xylB.