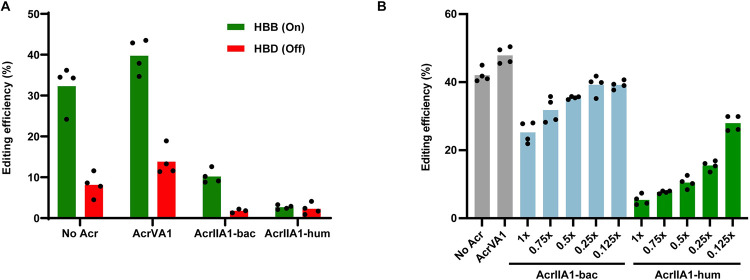
Fig 1. AcrIIA1 inhibits SpyCas9 editing in human cells.
(A) Editing by SpyCas9 of the HBB gene and the closely related off-target site HBD. AcrIIA1-bac uses the native bacterial codons. AcrIIA1-hum is codon optimized for human expression (P < 0.001). HEK293T cells were transiently transfected at a plasmid ratio of 1:2 SpyCas9:AcrIIA1 plasmid. (B) Dose-dependent inhibition of SpyCas9 editing of HBB by AcrIIA1. “x” represents the fold w/w plasmid amount of AcrIIA1 relative to SpyCas9. Total plasmid DNA transfected in each condition was constant. Bars represent the mean of biological replicates (dots). Underlying data can be found in S1 Data.