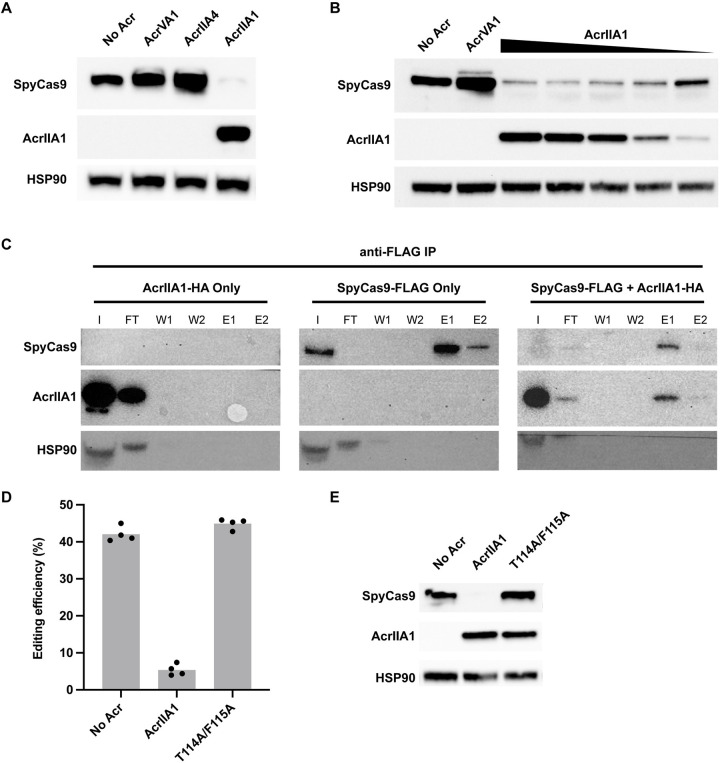
Fig 2. AcrIIA1-dependent degradation of SpyCas9.
(A) Western blot showing AcrIIA1-dependent decrease in SpyCas9 protein level in HEK293T cells. Expression of AcrIIA4 or AcrVA1 does not show a decrease in SpyCas9 protein. (B) Western blot showing the dose-dependent decrease in SpyCas9 protein with increasing expression of AcrIIA1 in HEK293T cells. AcrIIA1 plasmid is dosed from 1× to 0.125× relative to SpyCas9 plasmid. (C) Western blots of anti-FLAG immunoprecipitations pulling down FLAG-tagged SpyCas9 and probing for SpyCas9 and AcrIIA1. AcrIIA1-HA alone is fully eluted in the FT. SpyCas9-FLAG efficiently binds to the anti-FLAG beads and is eluted (E1 and E2). Co-expression of SpyCas9-FLAG and AcrIIA1-HA (1:0.125 plasmid ratio) results in lower SpyCas9. AcrIIA1 binds and elutes (E1 and E2) along with the residual SpyCas9. I = input, FT = flow through, W1 = wash 1, W2 = wash 2, E1 = elution 1, E2 = elution 2. (D) Editing by SpyCas9 on the HBB gene alone or in combination with AcrIIA1 or the AcrIIA1 double mutant T114A/F115A. Bars represent the mean of biological replicates (dots). Underlying data can be found in S1 Data. (E) Western blot showing the presence of SpyCas9 with the T114A/F115A AcrIIA1 double mutant.