Fig. 1. Phosphorylation-induced GFP phase separation-based FAK reporter visualizes endogenous activity of FAK in living cells and vertebrates.
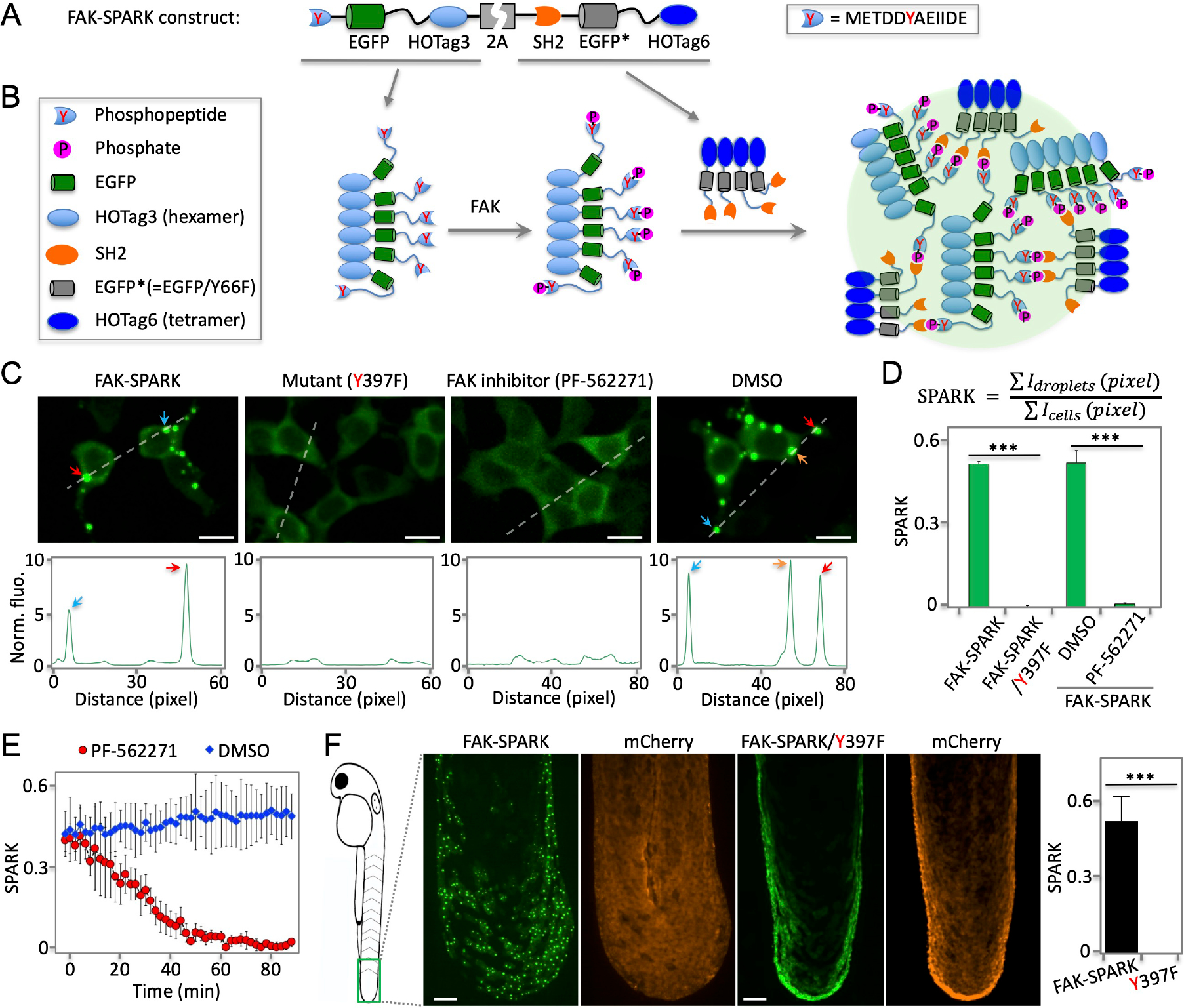
(A) Schematic of construct of FAK reporter FAK-SPARK (separation of phases-based activity reporter of kinase). HOTag: homo-oligomeric tag. (B) Cartoon showing working mechanism of FAK-SPARK. (C) Upper panels: (two left panels) fluorescence images of cells expressing FAK-SPARK, FAK-SPARK mutant Y397F that cannot be phosphorylated by FAK; (two right panels) fluorescence images of cells expressing FAK-SPARK incubated with FAK inhibitor or DMSO. Lower panels: histogram along the dash line. (D) Quantified SPARK signal in cells with various conditions. (E) FAK-SPARK is reversible upon addition of FAK inhibitor. (F) Fluorescence images of transgenic zebrafish expressing FAK-SPARK. Tg (UAS-FAK-SPARK) was crossed with Tg (ΔNp63:GAL4), and Tg (UAS-mCherry). Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3 or 4 biological replicates). ***: p value < 0.001. Scale bar, 20 μm (C, F).
