Fig. 1 |. Design principles of nanomaterial-based contrast agents for various imaging modalities and biomedical applications.
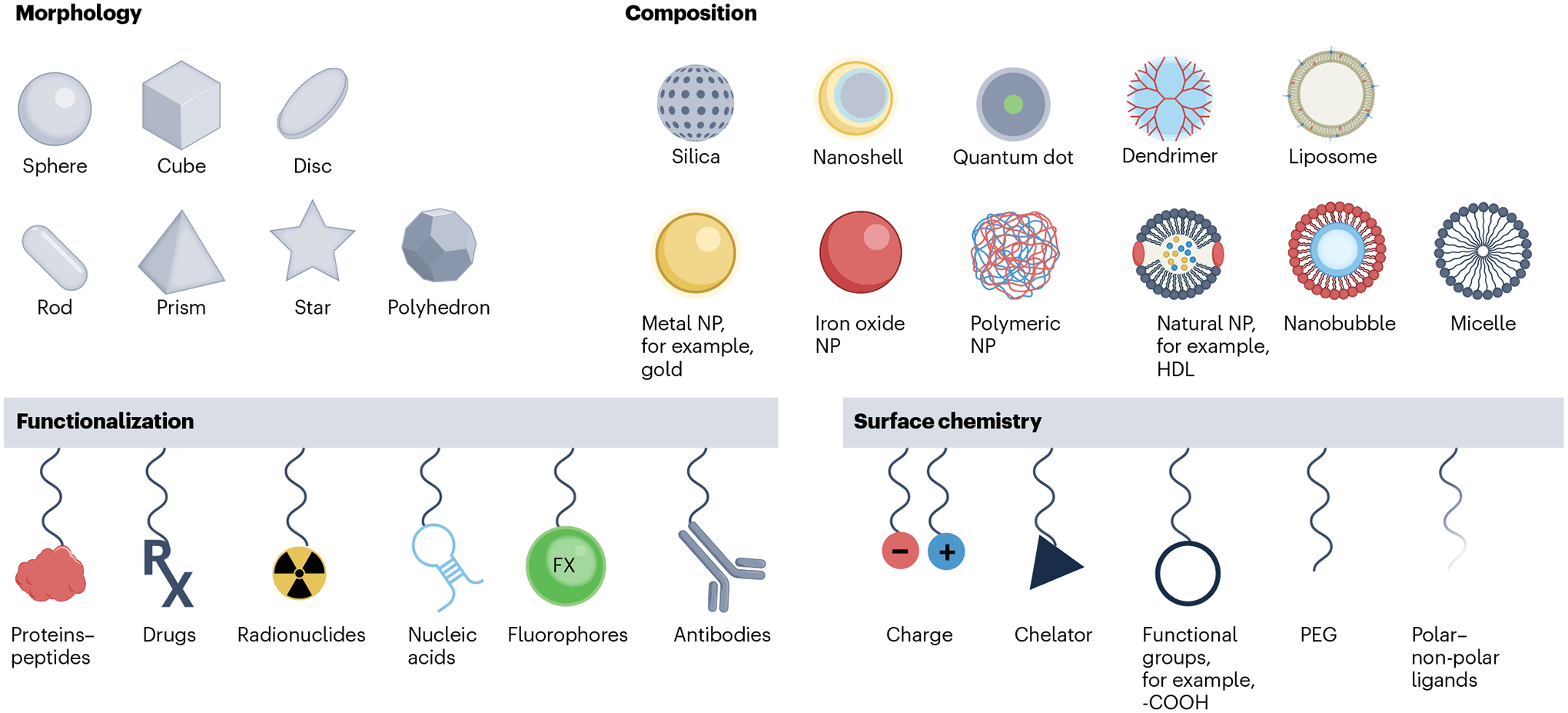
The physicochemical properties of nano-based contrast agents are generally described by their core and hydrodynamic diameter, chemical composition, shape, surface chemistry and functionalization. These agents are designed and optimized for major bioimaging modalities that produce contrast based on X-rays, radioactive decay, magnetism, optical photons and acoustics. These agents, in conjunction with the appropriate imaging techniques, are applied to provide structural and functional information of the disease in question. HDL, high-density lipoprotein; NP, nanoparticle; PEG, polyethylene glycol.
