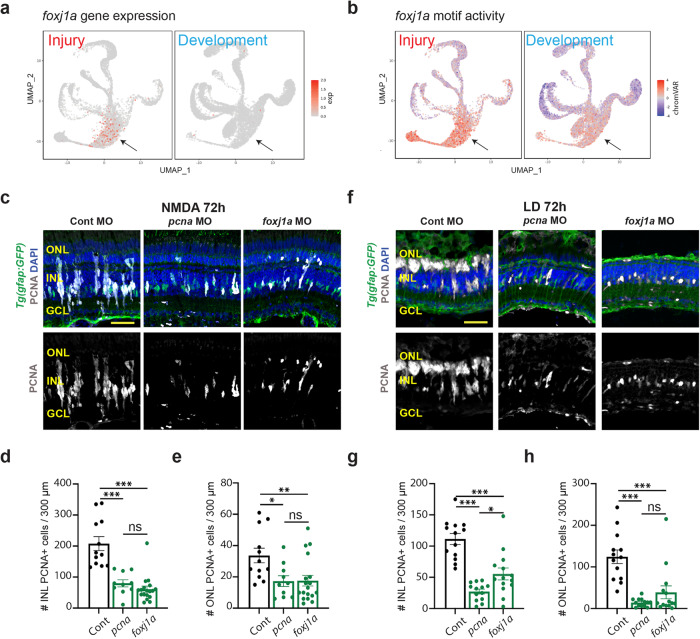
Fig. 7. foxj1a is required for MGPC proliferation.
a UMAPs showing the gene expression pattern of foxj1a between injury (left) and development model (right). b UMAPs showing the chromVAR motif activity of foxj1a between injury (left) and development model (right). c Tg(gfap:GFP) retinas electroporated with either Standard Control morpholino (Cont MO), pcna MO, or foxj1a MO were isolated 72 h after NMDA injection and immunostained for PCNA, GFP, and counterstained with DAPI. Outer nuclear layer (ONL); inner nuclear layer (INL); ganglion cell layer (GCL). d Quantification of the number of PCNA-labeled cells in the INL. Cont n = 12, pcna n = 10, foxj1a n = 18. Three independent experiments. e Quantification of the number of PCNA-labeled cells in the ONL. Cont n = 12, pcna n = 10, foxj1a n = 18. Three independent experiments. f Tg(gfap:GFP) retinas electroporated with either Cont MO, pcna MO, or foxj1a MO were isolated after 72 h of light damage (LD) and immunostained for PCNA, GFP, and DAPI. g Quantification of the number of PCNA-labeled cells in the INL. Cont and pcna n = 13, foxj1a n = 14. Three independent experiments. h Quantification of the number of PCNA-labeled cells in the ONL. Cont and pcna n = 13, foxj1a n = 14. Three independent experiments. Scale bars in (c) and (f) are 20 μm. d, e, g, h Data are presented as mean values ± SEM. For statistical analysis, one-way ANOVA was followed by t-test with Dunnett’s method for multiple comparisons correction. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences between the indicated groups (*p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001). Source data are provided as a Source Data file 1.