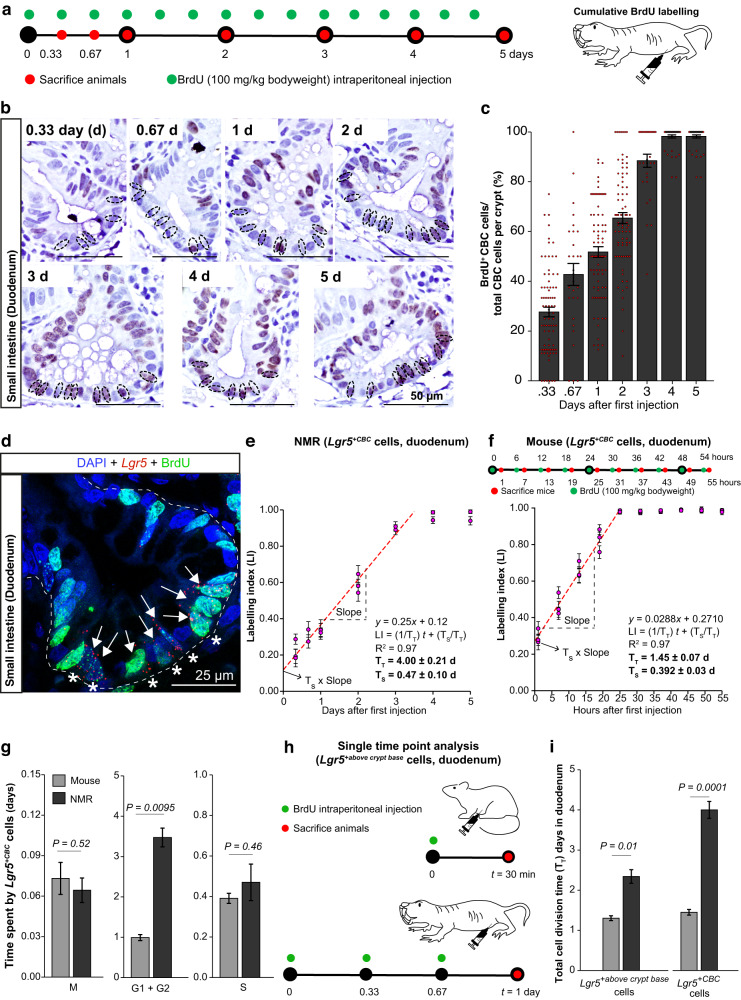
Fig. 3. Cytokinetics of Lgr5+CBC in the NMR small intestine.
a Schema showing BrdU injection schedule in NMRs (green) and time of tissue collection (red). b NMR crypts co-stained with anti-BrdU antibody (brown) and haematoxylin (blue). Dotted circles indicate crypt-based columnar (CBC) cells. c Bar graphs showing the mean percentage (±SEM) of labelled CBC cells (BrdU+CBC) at different time points in NMRs, derived by counting n = 20 crypts per animal (3 animals sacrificed at 0.33, 1, 2 days and 2 at 0.67, 3, 4, 5 days). d Immunofluorescent image showing Lgr5 mRNA (red), BrdU (green), and DAPI (blue) in NMR crypt injected with BrdU for 3 days. Asterisks (*) mark Lgr5+ cells at the crypt base (Lgr5+CBC) and white arrows indicate Lgr5+CBCBrdU+ cells. e Scatter plot showing a linear relationship between the ratio of Lgr5+CBCBrdU+ cells to the total number of Lgr5+CBC cells (labelling index) with time in NMRs until BrdU labelling becomes saturated. Each data point represents the mean (±SEM) of 20 crypts counted per animal (n = 3 animals at 0.33, 1 and 2 days; n = 2 at 0.67, 3, 4 and 5 days). f Top, BrdU injection times in mice (green) and time points when small intestinal tissues were collected (red). Bottom, scatter plot showing a linear increase in BrdU labelled murine Lgr5+CBC cells with time. Each dot denotes the mean (±SEM) of 30 crypts counted per animal (n = 3 animals/time point). g Bar graphs (mean ± SEM) showing the length of specific cell cycle phases of mouse and NMR Lgr5+CBC cells. Exact P-values have been indicated on the graphs. h Schema showing the experimental design for estimating the total cell cycle time, TT, of Lgr5+ cells located above the crypt base by injecting BrdU (green) in mice and NMRs and time points when tissues were collected (red). i Bar graphs showing the mean (±SEM) TT of Lgr5+ cells above the crypt base (left) and Lgr5+CBC (right) in mice and NMRs. Exact P-values have been indicated on the graphs. Statistical significance was determined by performing Student’s t-tests using two-tailed, unpaired and unequal variance. Scale bars are indicated on the images (25 µm or 50 µm).