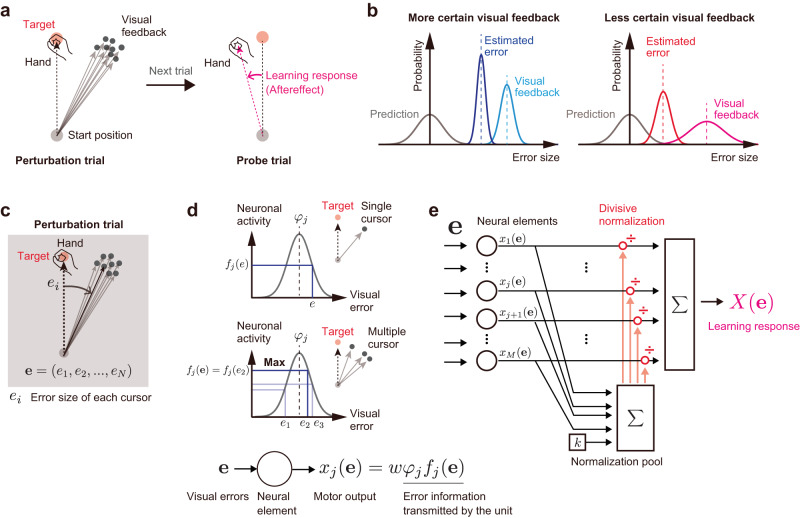
Fig. 1. The divisive normalization (DN) mechanism processing visual prediction errors.
a In previous studies, uncertain visual feedback was provided by a population of dots (cursors). The learning response to such uncertain visual feedback can be evaluated by measuring the movement direction (i.e., the aftereffect or learning response herein). b According to the maximum likelihood estimation scheme, the motor system estimates the error by combining the actual visual information with the visual information predicted by the motor command. The more uncertain the visual information, the smaller the estimated error, which reduces the learning response. c–e Proposed model. c We consider that each cursor conveys different visual error information. d Each neuronal element encodes the visual error according to the Gaussian tuning function with the maximum operation [φjfj(e)] and transforms the error information to a motor output [xj(e)]. e In the DN model, the outputs of the elements are normalized by a DN mechanism before being integrated to produce the learning response.