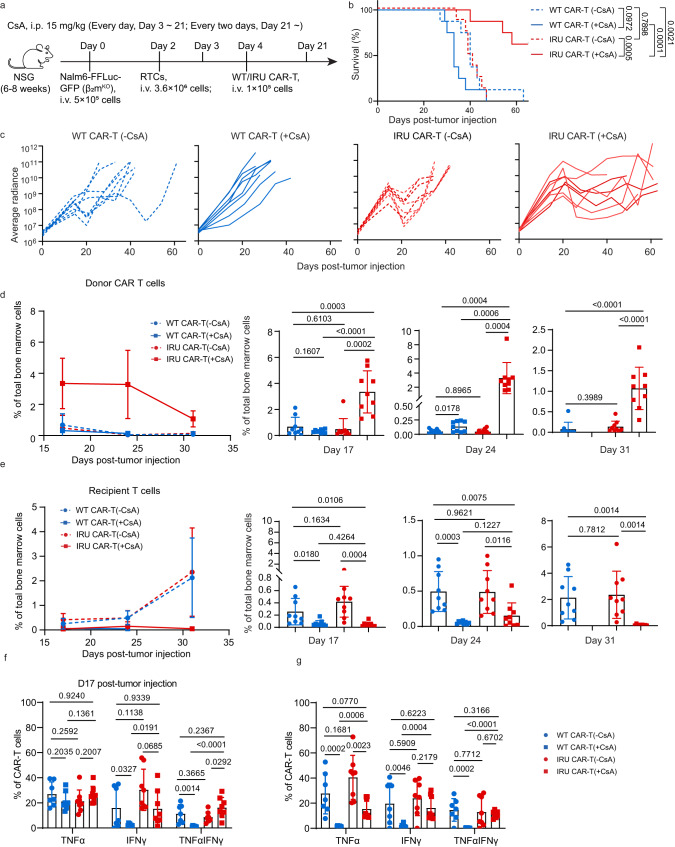
Fig. 5. IRU CAR-T cells retained anti-leukemia functions in the presence of recipient T cells in vivo by using CsA.
a Schematic of ALL NOD.Cg-PrkdcscidIl2rgem1Smoc (NSG) (female, aged 8-12 weeks) model with RTCs for (b–g). b Kaplan–Meier analysis of the mice survival in mice treated with WT CAR-T cells (+/-CsA) and IRU CAR-T cells (+/-CsA) (n = 8 animals in two batches). c Tumour burden (average radiance, ph/s) in each experimental group (n = 8 animals in two batches). d, e Frequencies of donor CAR-T cells (d) and recipient T cells (e) in bone marrow (left, curve chart; right, column charts) over time (n = 9 animals in two batches). f, g Cytokine detection of donor CAR-T cells in each group at Day 17 (f) and 24 (g) upon stimulation with PMA/Ionomycin for 4 hrs (n = 8 animals in two batches in each group, except n = 7 animals in two batches in WT CAR-T (-CsA) group). All data are means±s.d. P values were determined by Mantel-Cox log-rank test (b) or two-tailed Unpaired t test (d, e) or Multiple t test adjusted by the Holm-Sidak method (f, g). WT CAR-T (-CsA) as blue circle, WT CAR-T (+CsA) as blue square, IRU CAR-T (-CsA) as red circle and IRU CAR-T (+CsA) as red square. Abbreviations: i.v. intravenous injection; i.p. intraperitoneal injection.