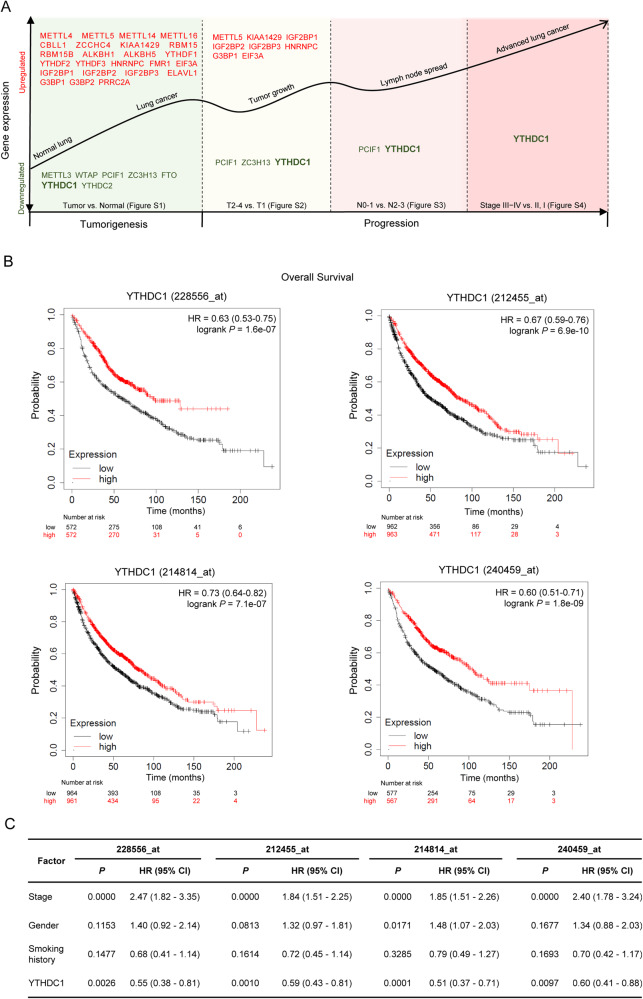
Fig. 1. YTHDC1 is negatively correlated with the progression of lung cancer.
A The expression patterns of m6A “writers” (METTL3, METTL4, METTL5, METTL14, METTL16, WTAP, KIAA1429, RBM15, RBM15B, ZC3H13, CBLL1, ZCCHC4, and PCIF1), “erasers” (ALKBH1, ALKBH5, and FTO) and “readers” (YTHDC1, YTHDC2, YTHDF1, YTHDF2, YTHDF3, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPC, FMR1, EIF3A, IGF2BP1, IGF2BP2, IGF2BP3, ELAVL1, G3BP1, G3BP2, and PRRC2A) along the tumor progression of lung cancer are analyzed using the GTEx Portal (version V8) and TCGA (version 2019-7-20) databases. B Kaplan–Meier curves for overall survival of lung cancer patients with high and low expression levels of YTHDC1 using the Kaplan–Meier Plotter (KMplot) program (www.kmplot.com, version 2022). The median gene expression values as the cutoff. Four probes (228556_at, 212455_at, 214814_at and 240459_at) targeting YTHDC1 are used. C The association between YTHDC1 with overall survival in lung cancer is analyzed using multivariate Cox proportional-hazards regression analysis after adjustment for tumor stage, gender, and smoking history. Four probes (228556_at, 212455_at, 214814_at and 240459_at) targeting YTHDC1 are used.