FIGURE 2.
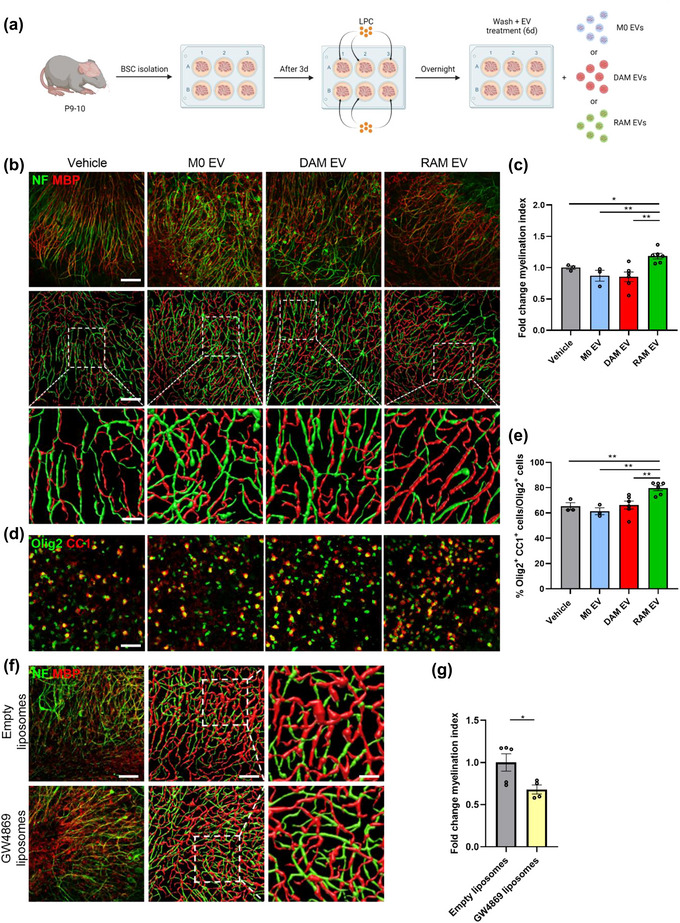
Extracellular vesicles released by RAMs improve remyelination in cerebellar brain slices. (a) Schematic representation showing the isolation and culture of cerebellar brain slices as well as their stimulation with vehicle (PBS), or extracellular vesicles (EVs) released by naive macrophages (M0, PBS‐treated), disease‐associated macrophages (DAMs, LPS‐stimulated) and repair‐associated macrophages (RAMs, IL‐4‐stimulated). LPC = lysolecithin, demyelinating compound. Created with biorender.com. (b, d) Representative images and three‐dimensional reconstruction of immunofluorescent MBP/NF (b) and Olig2/CC1 (d) stains of cerebellar brain slices treated with vehicle or EVs isolated from M0, DAMs and RAMs. Slices were treated with 4 × 109 EVs/mL. Scale bars, 100 µm (b, (row 1, 2) d); 25 µm (b, row 3). (c) Relative number of MBP+ NF+ axons out of total NF+ axons in cerebellar brain slices treated with vehicle or EVs released by M0, DAMs and RAMs (n = 3–6 slices). (e) Percentage Olig2+ CC1+ cells within the Olig2+ cell population in cerebellar brain slices treated with vehicle or EVs released by M0, DAMs and RAMs (n = 3–6 slices). (f) Representative images and three‐dimensional reconstruction of immunofluorescent MBP/NF of cerebellar brain slices treated with empty liposomes or GW4869 liposomes. Scale bars, 100 µm (column 1, 2); 25 µm (column 3). (g) Relative number of MBP+ NF+ axons out of total NF+ axons in cerebellar brain slices treated with empty liposomes or GW4869 liposomes (n = 4–5 slices). Results are pooled from or representative of three independent experiments. Data are represented as mean ± SEM and statistically analysed using the Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn's multiple comparison test (c, e) or the Mann‐Whitney test (g). *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.
