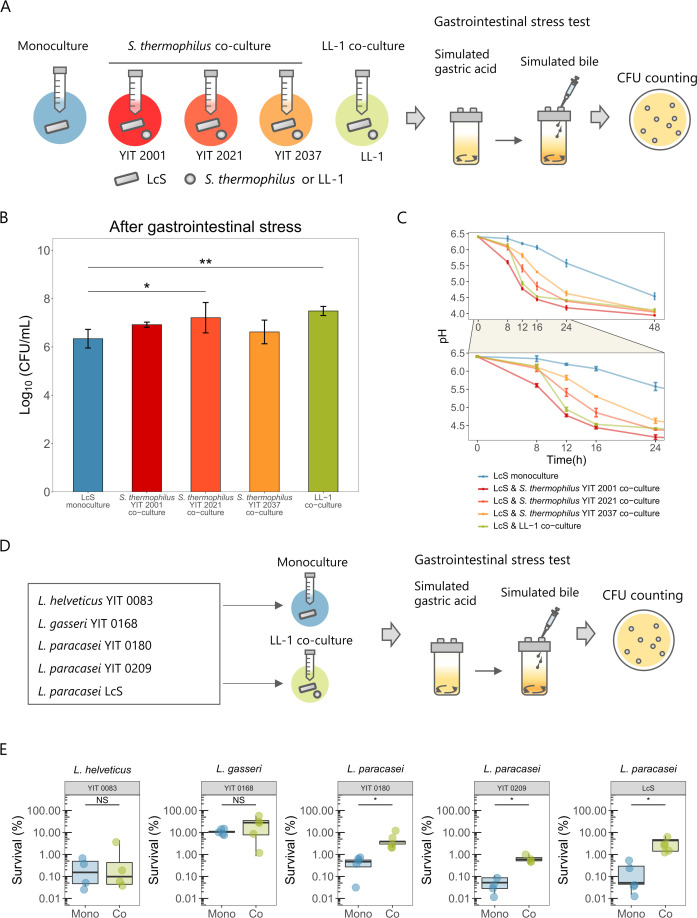
Fig 3.
Stress tolerance through co-culture in various combinations. (A) LcS was co-cultured with Streptococcus thermophilus YIT 2001, YIT 2021, or YIT 2037 in addition to being monocultured or co-cultured with LL-1. After 48 h of culture, a simulated gastrointestinal stress test was performed. (B) Log10 (CFU/mL) of LcS after simulated gastrointestinal stress (mean ± SD, n = 4). (C) pH changes under the five culture conditions (mean ± SD, n = 3). The lower panel is an enlarged view of the 0- to 24-h period. (D) In addition to LcS, Lactobacillus helveticus YIT 0083, Lactobacillus gasseri YIT 0168, Lacticaseibacillus paracasei YIT 0180, or Lacticaseibacillus paracasei YIT 0209 were monocultured or co-cultured with LL-1. After 48 h of culture, a simulated gastrointestinal stress test was performed. Simulated gastric acid at pH 4.0 was used for all strains, and oxgall concentrations of 0.16% (YIT 0083 and YIT 0209) and 0.30% (YIT 0168, YIT 0180, and LcS) were used as simulated bile. (E) Percentage of bacteria surviving after the simulated gastrointestinal stress in each strain (mean ± SD, n = 4 or 5). (B) Statistical significances relative to LcS monoculture were determined by using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (**P < 0.01 and *P < 0.05). (E) Statistical significances were determined by using two-tailed Welch’s t-test (*P < 0.05 and NS, not significant).