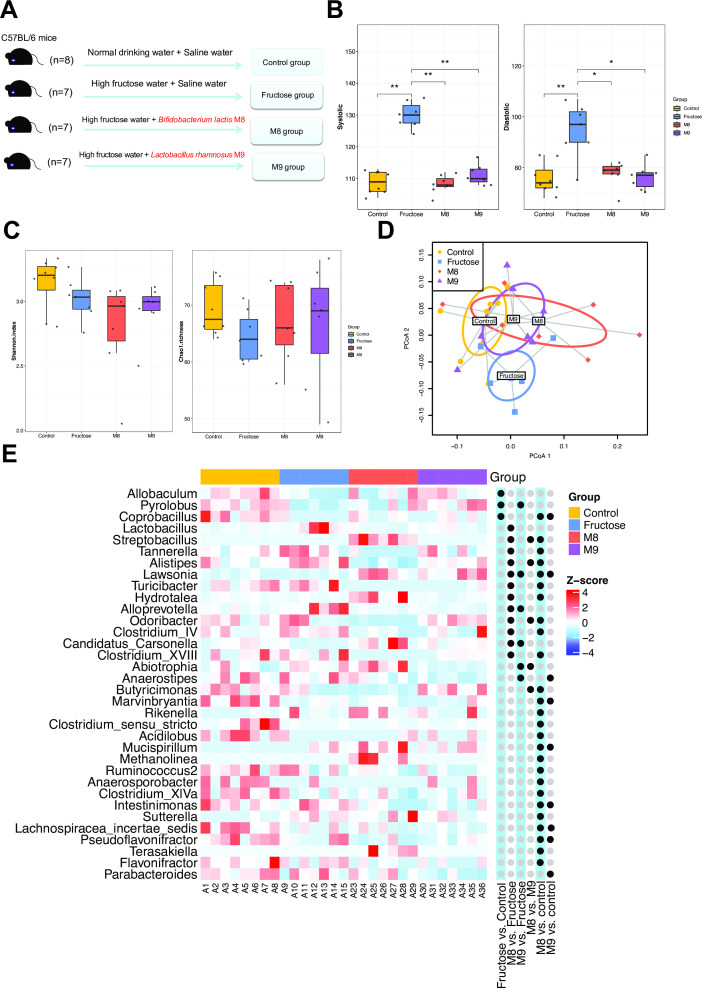
Fig 1.
Probiotics reduce blood pressure level through modulating the composition of gut microbiota. (A) The experiment design of this study; (B) the blood pressure level (left: SBP, right: DBP) after 16-week intervention; Wilcoxon test was used to detect the significant change in blood pressure between groups: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. (C) Microbial diversity (left: Shannon index, right: Chao1 richness) of gut microbial community at genus level after 16-week intervention; (D) principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) analysis indicated the difference in overall composition of gut microbial community among the groups using weighted UniFrac distance; (E) heatmap of genus showing differential abundance in at least one pairwise comparison using Wilcoxon test. For visualization, the abundance levels were log-transformed then centered and scaled to a mean of 0 and standard deviation of 4. Black dots indicate the significance level of the comparison (false discovery rate (FDR) <0.25).