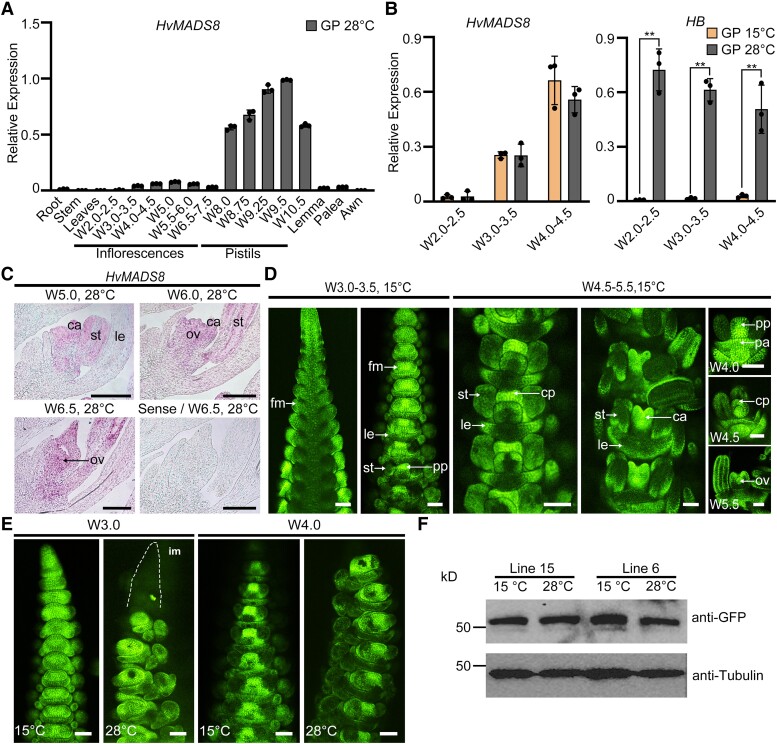
Figure 3.
Temporal and spatial expression of HvMADS8 at different temperatures. A) Relative expression of HvMADS8 in different GP plant tissues and at different stages of development at 28 °C. Values are means ± Sd; n = 3 biological replicates. B) Relative expression of HvMADS8 at early stages of inflorescence development at 15 and 28 °C. Expression of HB (temperature-responsive gene) was used as positive control. Values are means ± Sd; n = 3 biological replicates. Asterisks indicate significant differences (2-way ANOVA test; **P < 0.01). C) In situ hybridization showing expression of HvMADS8 at stages W5.0 to 6.5 at 28 °C in longitudinal sections of GP florets. The sense probe served as a negative control. ca, carpel; le, lemma; ov, ovule; st, stamen. Scale bars, 100 μm. D) Accumulation of HvMADS8 in spikes and florets from W3.0 to 5.5 in proHvMADS8:HvMADS8-eGFP transgenic lines at 15 °C. cp, carpel primordia; fm, floral meristem; pa, palea; pp, pistil primordia. Scale bars, 100 μm. E) Accumulation of HvMADS8 in W3.0 and W4.0 proHvMADS8:HvMADS8-eGFP transgenic spikes grown at 15 and 28 °C. im, inflorescence meristem. Scale bars, 100 μm. F) Immunoblot analysis of HvMADS8-eGFP abundance in W5.5 to 6.5 spikes from 2 independent proHvMADS8:HvMADS8-eGFP lines grown at 15 and 28 °C. Tubulin served as loading control. All experiments were independently performed at least 3 times with similar results.