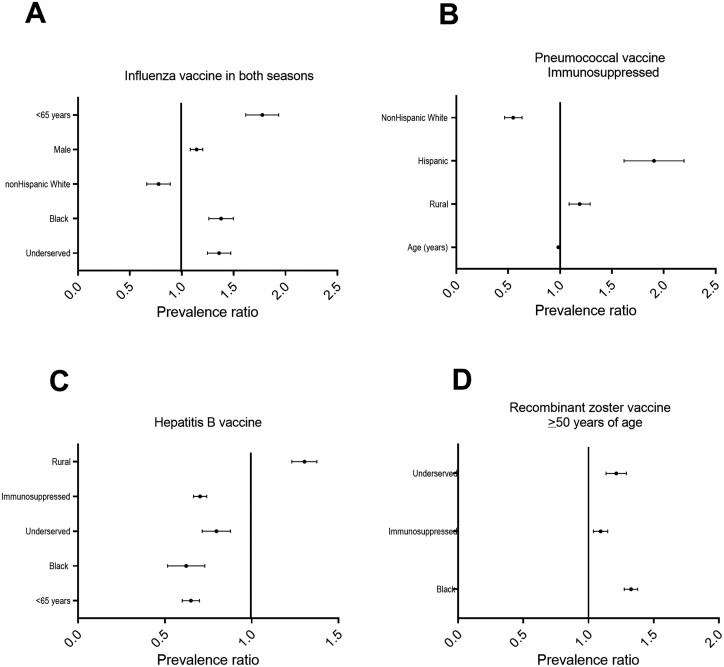
Figure 2.
Prevalence ratios (PR) for factors for receiving adult vaccines. A. Influenza vaccine in both 2017–2018 and 2018–19 seasons. Older age (PR 0.98; 95% confidence interval (95%CI) 0.98–0.99; P < .001), and non-Hispanic White patients (PR 0.76, 95% CI 0.59–0.98, P < .03) were significantly more likely to receive the influenza vaccine in both seasons. Male patients (PR 1.14; 95%CI 1.04–1.25; P = .004), Black patients (PR 1.37; 95%CI 1.18–1.59; P < 0.001) and those living in underserved geographic areas (PR 1.35; 95%CI 1.17–1.56; P < 0.001) were less likely to be immunized against influenza in both seasons. B. Pneumococcal vaccines (both pneumococcal conjugate 13-valent and pneumococcal polysaccharide 23-valent vaccines as recommended for immunosuppressed patients). Younger age PR 0.98; (95%CI 0.98–0.99; P < .001), and those who were not non-Hispanic White patients (PR 0.54; 95% CI 0.41–0.70; P < .001) were significantly more likely to have not completed the pneumococcal vaccine series. Hispanic patients were less likely to have completed the series compared to all others (PR 1.86; 95% CI 1.42–2.43; P < .001). Those living in rural areas were less likely to have completed the series (PR 1.18; 95% CI 1.02–1.37; P = .03). C. Hepatitis B vaccine. Unlike other vaccines, Black patients (PR 0.60; 95%CI 0.45–0.80; P < 0.001), patients on immunosuppressive therapy (PR 0.70; 95%CI 0.64–0.77; P < .001) and those living in an underserved area (PR 0.79; 95%CI 0.66–0.94; P = .009) were all associated with hepatitis B vaccine uptake. Patients who were older in age (PR 1.02; 95%CI 1.02–1.02; P < .001), non-Hispanic White (PR 1.19; 95%CI 1.00–1.40; P = .05) and rural-dwelling (PR 1.30; 95%CI 1.18–1.43; P < .001) were associated with less likely to have completed the hepatitis B vaccine series. D. Recombinant zoster vaccine for those aged 50 years and older. Black patients (PR 1.32; 95% 1.24–1.42; P < .001), patients on immunosuppressive therapy (PR 1.09; 95% CI 1.00–1.19; P = .05) and those living in an underserved area (PR 1.21; 95%CI 1.08–1.35; P = 0.001) were less likely to have received the recombinant zoster vaccine series.