Fig. 3.
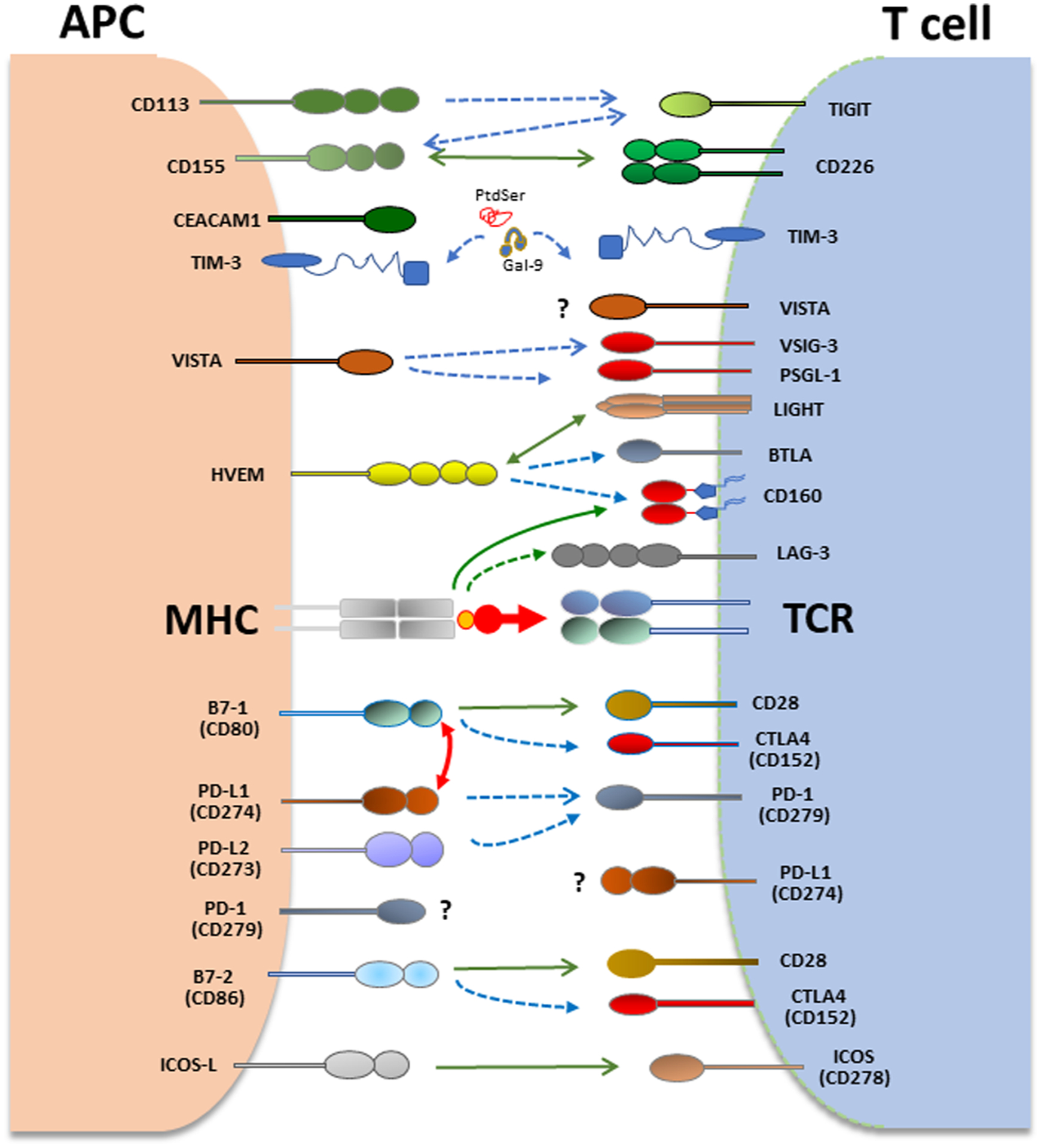
Coinhibitory pathways in T cells and APC. T cell activation is initiated by recognition of antigens presented by antigen-presenting cells (APCs) to the T cell receptor (TCR)/CD3 complex. CD28 is the prototype costimulatory receptor in T cells and interacts with CD80 and CD86. Many coinhibitory receptors are upregulated upon T cell activation and can attenuate TCR and costimulatory signals. CTLA4 and PD-1 are the prototype co-inhibitory receptors expressed in T cells. CTLA-4 interacts with B7–1 (CD80) and B7–2 (CD86) whereas PD-1 (CD279) interacts with PD-L1 (CD274) and PD-L2 (CD273) to inhibit T cell responses. In addition to canonical interaction of PD-L1 with PD-1 in trans, PD-L1 interacts with B7–1 (CD80) in cis, when co-expressed on the same APC leading to diminished availability of PD-L1 for canonical interaction with PD-1 in trans. VISTA, TIM-3 and PD-1 are expressed both in T cells and APC and can regulate immune responses by altering the properties of myeloid cells and T cells.
