Figure 1.
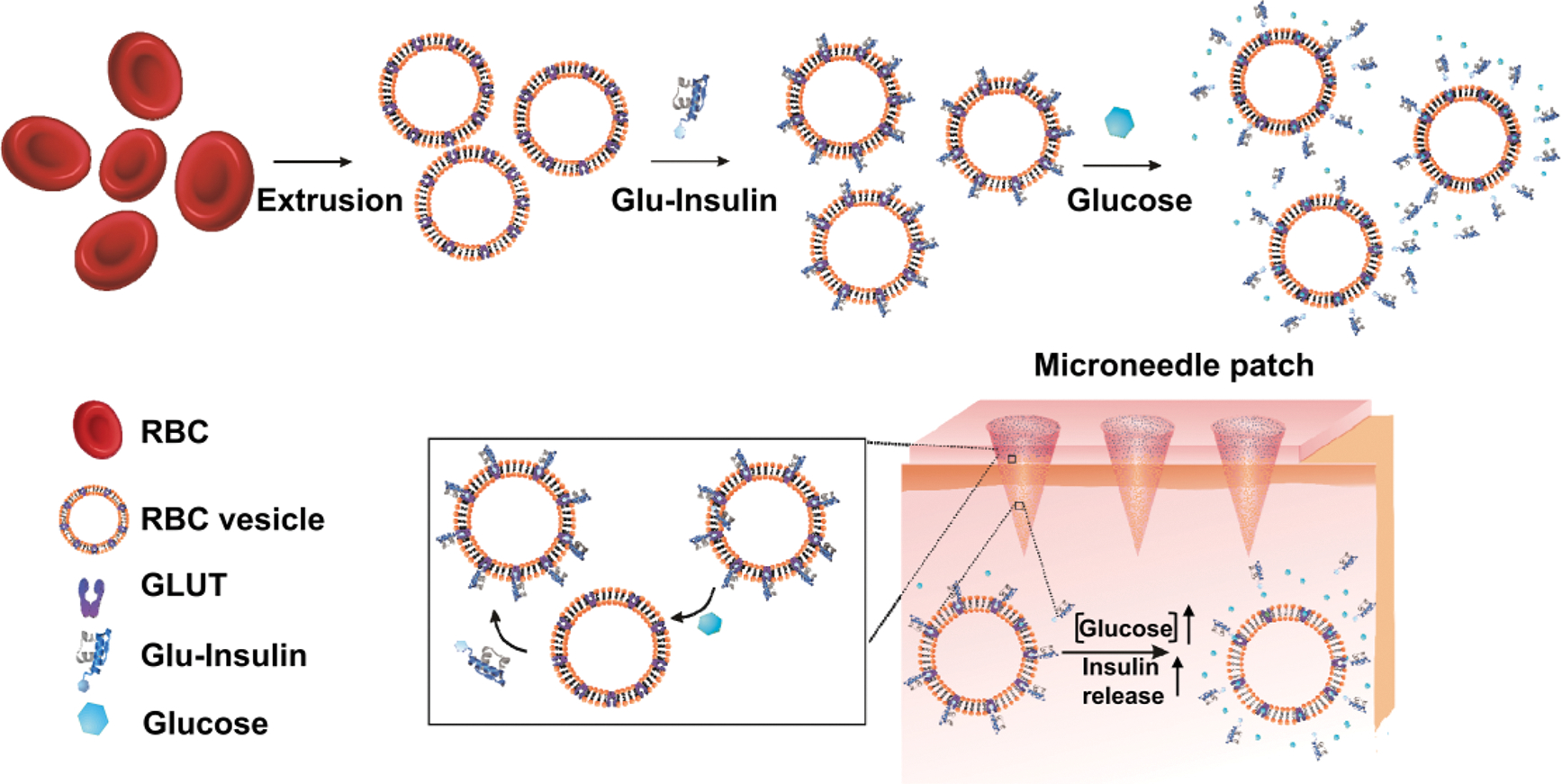
Schematic showing the glucose-responsive insulin delivery system utilizing a microneedle-array patch encapsulated with red blood cell (RBC) vesicles bound with glucosamine-modified insulin (Glu-Insulin) together with additional free Glu-Insulin. Glu-Insulin can be quickly released under hyperglycemic conditions owing to the competitive interaction between Glu-Insulin and glucose. The additional Glu-Insulin loaded in the upper layer is expected to further bind to GLUT expressed on RBC vesicles, similar to a “recharge” process for further glucose-responsive release.
